A trial balance tells the company its unadjusted balances in each account. The unadjusted trial balance is then carried forward to the fifth step for testing and analysis. Companies may also choose between single-entry accounting vs. double-entry accounting. Double-entry accounting is required for companies building out all three major financial statements, the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
Posting From Journal to Ledger Accounts
What is Journalizing and posting in accounting?
May 21, 2019. Posting in accounting is when the balances in subledgers and the general journal are shifted into the general ledger. Posting only transfers the total balance in a subledger into the general ledger, not the individual transactions in the subledger.
Another potential error is that a transaction was entered twice. Nevertheless, once the trial balance is prepared and the debits and credits balance, the next step is to prepare the financial statements.
Now, the starting point of all of this process is at recording the business transactions in the general journal. The last two steps in the accounting process are preparing a trial balance and then preparing the balance sheet and income statement. This information is provided in order to communicate the financial position of the entity to interested parties. In the beginning, we talked about the procedure of recording a transaction.
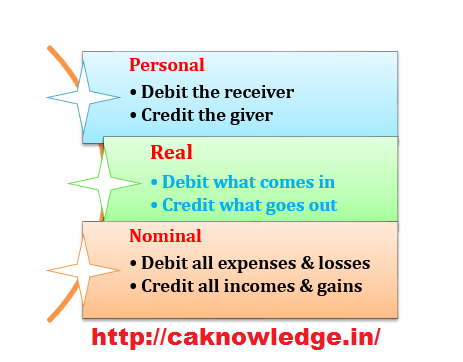
A debit is an accounting entry that results in either an increase in assets or a decrease in liabilities on a company’s balance sheet. In fundamental accounting, debits are balanced by credits, which operate in the exact opposite direction. The income statement is prepared using the revenue and expense accounts from the trial balance.
This information entered into the journal and summarised into the ledger is then aggregated further into a trial balance, which is used to generate the financial statements of the business entity. Cash accounting requires transactions to be recorded when cash is either received or paid. Double-entry bookkeeping calls for recording two entries with each transaction in order to manage a thoroughly developed balance sheet along with an income statement and cash flow statement. As business transactions occur during the year, they are recorded by the bookkeeper with journal entries.
An accounting ledger refers to a book that consists of all accounts used by the company, the debits and credits under each account, and the resulting balances. The first step is to enter the account name and number on the ledger form. A company’s two main financial statements, income statement and balance sheet, have different accounts. In this step of the accounting cycle an accountant takes total credits and debits recorded in categorized sub-ledgers and posts them into the general ledger to be used for official accounting statements.
A trial balance is a bookkeeping worksheet in which the balance of all ledgers are compiled into debit and credit account column totals that are equal. A company prepares a trial balance periodically, usually at the end of every reporting period. The general purpose of producing a trial balance is to ensure the entries in a company’s bookkeeping system are mathematically correct.
With the abundance of technological advancements in the fields of software, there are numerous accounting solutions provided by many technology giants like Oracle Suite, Tally, etc. Most of such software products provide a centralized repository to log entries into journals and ledger. Due to such accountancy software products, recording transactions have become far easier. There is no need to maintain all the books separately and reconcile manually as this software help in automating such redundant manual tasks. First, the business transaction is recorded in the general journal and then the entry is posted in respective accounts in the general ledger.
After an entry is made, the debit and credit are added to a T-account in the categorized journal. At the end of a period, the T-account balances are transferred to the ledger where the data can be used to create accounting reports. Double entry system of bookkeeping says that every transaction affects two accounts. There is a proper procedure for recording each financial transaction in this system, called as accounting process.The process starts from journal followed by ledger, trial balance, and final accounts.
However, this does not mean there are no errors in a company’s accounting system. For example, transactions classified improperly or those simply missing from the system could still be material accounting errors that would not be detected by the trial balance procedure. It is important to note that just because the trial balance balances, does not mean that the accounts are correct or that mistakes did not occur. There might have been transactions missed or items entered in the wrong account – for example increasing the wrong asset account when a purchase is made or the wrong expense account when a payment is made.
Both of these books of accounts provide a way to record business transactions through the double-entry accounting system via debits and credits. It is the entry point for any kind of business transaction to make its way into the books of accounts of the company before it flows to the next level of classification of transactions in accountancy.
Such uniformity guarantees there are no unequal debits and credits that have been incorrectly entered during the double-entry recording process. However, a trial balance cannot detect bookkeeping errors that are not simple mathematical mistakes. Companies initially record their business transactions in bookkeeping accounts within the general ledger.
- However, a trial balance cannot detect bookkeeping errors that are not simple mathematical mistakes.
- Such uniformity guarantees there are no unequal debits and credits that have been incorrectly entered during the double-entry recording process.
It must be noted that there is a concept of duality in accounts that results in a double-entry accounting system. Hence, every business transaction is recorded in such a way that it affects two accounts in terms of credit and debit entry. In the world of finance, accountancy is one stickler field in which all the norms and laws are required to be followed both in spirit and text. The main financial statements include an income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. In order to compile the financial statements of a business entity, there are numerous stages of measuring, recording and presenting the reconciled form of every business transaction.
After the balances for accounts are calculated, the entries are transferred from general ledger to trial balance. At the end of the accounting period, atrial balanceis calculated as the fourth step in the accounting cycle.
BUSINESS IDEAS
If an income statement is prepared before an entity’s year-end or before adjusting entries (discussed in future lessons) it is called an interim income statement. The income statement needs to be prepared before the balance sheet because the net income amount is needed in order to fill-out the equity section of the balance sheet. The net income relates to the increase (or in the case of a net loss, the decrease) in owner’s equity. As per the convention followed, left the side of the T-shaped table usually contains the debit entries, the right of the T-shaped table contains the credit entries. Many companies also mentioned some journal-specific information into a general ledger like serial numbers, dates, and description of the transaction.
The debits and credits include all business transactions for a company over a certain period, including the sum of such accounts as assets, expenses, liabilities, and revenues. A trial balance is a worksheet with two columns, one for debits and one for credits, that ensures a company’s bookkeeping is mathematically correct.
A trial balance also uncovers errors in journalizing and posting and is useful in preparing financial statements. SequentiallyAccount-wiseDebit and CreditColumnsSidesNarrationMustNot necessary.BalancingNeed not to be balanced.Must be balanced. The general ledger is more of a summary at the account level of every business transaction which comes from various journals containing chronological accounting entries.
AccountingTools
Depending on the kinds of business transactions that have occurred, accounts in the ledgers could have been debited or credited during a given accounting period before they are used in a trial balance worksheet. Furthermore, some accounts may have been used to record multiple business transactions. As a result, the ending balance of each ledger account as shown in the trial balance worksheet is the sum of all debits and credits that have been entered to that account based on all related business transactions. Preparing a trial balance for a company serves to detect any mathematical errors that have occurred in the double-entry accounting system. If the total debits equal the total credits, the trial balance is considered to be balanced, and there should be no mathematical errors in the ledgers.
A trial balance is a list and total of all the debit and credit accounts for an entity for a given period – usually a month. The format of the trial balance is a two-column schedule with all the debit balances listed in one column and all the credit balances listed in the other. The trial balance is prepared after all the transactions for the period have been journalized and posted to the General Ledger. A trial balance is a list of accounts and their balances at a given time. Its primary purpose is to prove the equality of debits and credits after posting.
At the end of an accounting period, the accounts of asset, expense or loss should each have a debit balance, and the accounts of liability, equity, revenue or gain should each have a credit balance. On a trial balance worksheet, all the debit balances form the left column, and all the credit balances form the right column, with the account titles placed to the far left of the two columns.
ACCOUNTING
If any of the above steps is missing, then it would be hard to prepare the final accounts. Debits and credits of a trial balance being equal ensure there are no mathematical errors, but there could still be mistakes or errors in the accounting systems.
Journal and Ledger are the two pillars which create the base for preparing final accounts. The Journal is a book where all the transactions are recorded immediately when they take place which is then classified and transferred into concerned account known as Ledger. The main difference between them is that the general journal serves as the initial book of entry.