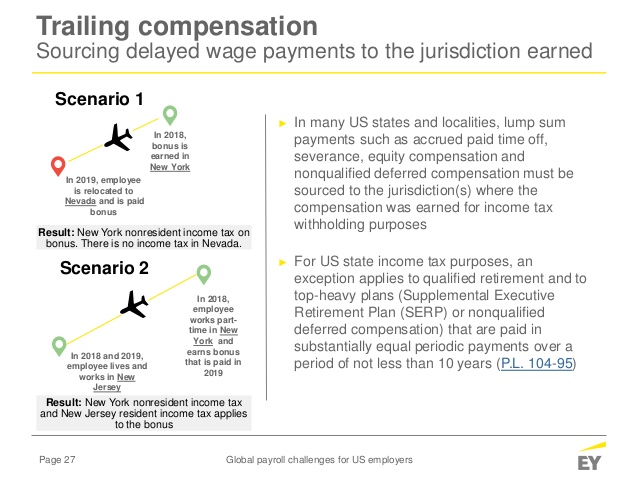
In some states there are cities, counties, and other local governmental units that impose their own income tax. If you do business in one of these localities, you may very well have an additional income tax withholding obligation. In addition to local income taxes, you may also find yourself paying local taxes measured by your total payroll (payroll expense taxes) or withholding local occupational fees from your employees’ wages. There are several sets of neighboring income tax states that do not share a reciprocal income tax agreement.
Form W-4: Understanding Your W-4 Form
In the US, withholding by employers of tax on wages is required by the federal, most state, and some local governments. Taxes withheld include federal income tax, Social Security and Medicare taxes, state income tax, and certain other levies by a few states. However, the IRS has made revisions to the Form W-4 for 2020. The new version removes the use of allowances, along with the option of claiming personal or dependency exemptions.
You may not have had enough withholding or deductions. This leaves more income to be taxed resulting in a lower refund or the need to pay additional taxes with your return. If you had unemployment, that is also taxable.
Employers must file a quarterly report of aggregate withholding taxes, Form 941, with the Internal Revenue Service. This report includes income, Social Security, and Medicare tax totals for the quarter. Partnerships making payments for partners must file Form 8813 quarterly.
Income tax withheld on wages is based on the amount of wages less an amount for declared withholding allowances (often called exemptions). Withholding for allowances are calculated based on the assumption of a full year of wages. Amounts of tax withheld are determined by the employer.
Wage withholding is based on wages actually paid and employee declarations on federal and state Forms W-4. Social Security tax withholding terminates when payments from one employer exceed the maximum wage base during the year. Social Security tax is withheld from wages at a flat rate of 6.2% (4.2% for 2011 and 2012). Wages paid above a fixed amount each year by any one employee are not subject to Social Security tax. Medicare tax of 1.45% is withheld from wages, with no maximum.
Form 1040 will provide opportunities to take advantage of all deductions and credits that apply to you. Filling our the form will also let you know if you will owe any additional taxes or receive a refund.
How is state tax withholding calculated?
State Withholding Tax. Both state and local governments can impose withholding on wage income, but they can only do so based on their own tax rates. You can have both state and federal income taxes withheld, but you cannot have state taxes withheld and federal taxes withheld twice at both levels.
Type of federal return filed is based on taxpayer’s personal situation and IRS rules/regulations. Additional fees apply with Earned Income Credit and you file any other returns such as city or local income tax returns, or if you select other products and services such as Refund Transfer. Valid for 2017 personal income tax return only.
States that tax income also tax non-residents for their in-state earnings. In addition to earned income, other reasons a non-resident might be required to file a non-resident return and pay taxes are earnings from a partnership or “S” Corporation, or gambling winnings. In addition, if income taxes were withheld in error, the only way to recover them is to file the state’s non-resident income tax return and claim the refund. The justification for taxing non-residents’ income is that commuters put a significant strain on state services and infrastructure.
Tax Withholding: Good For Government, Bad For Taxpayers
Return must be filed January 5 – February 28, 2018 at participating offices to qualify. Type of federal return filed is based on your personal tax situation and IRS rules. Additional fees apply for Earned Income Credit and certain other additional forms, for state and local returns, and if you select other products and services. Visit hrblock.com/ez to find the nearest participating office or to make an appointment. The amount of tax withheld is based on the amount of payment subject to tax.
Do I need to withhold state taxes?
There is no issue for residents of a non-income tax state who work in a state that taxes income: they must pay non-resident taxes to the state where they earned their income. State income taxes are withheld from salaries and wages, and taxpayers must file an annual income tax return to settle up.
Purchasers of U.S. real estate must withhold 10% of the sales price from payments to foreign sellers. This amount can be reduced to the anticipated federal income tax due, upon advance application on Form 8288-B to the Internal Revenue Service. These payments are treated like estimated tax payments, and the foreign person must still file a U.S. tax return reporting any gain or loss. In addition, partnerships are required to make tax payments (referred to as withholding) on behalf of foreign partners.
- Withholding for allowances are calculated based on the assumption of a full year of wages.
- Amounts of tax withheld are determined by the employer.
- Income tax withheld on wages is based on the amount of wages less an amount for declared withholding allowances (often called exemptions).
(This brings the total federal payroll tax withholding to 7.65%.) Employers are required to pay an additional equal amount of Medicare taxes, and a 6.2% rate of Social Security taxes. You might even have to make quarterly payments in addition to withholding from your benefits.
It does not provide for reimbursement of any taxes, penalties, or interest imposed by taxing authorities and does not include legal representation. Additional terms and restrictions apply; See Free In-person Audit Support for complete details.
These payments are required regardless of whether income is actually distributed to the partner. Payments are also required quarterly or at year end for business income or other undistributed income. Partnership payments on business income are treated like estimated tax payments, and the foreign person must still file a U.S. tax return reporting the business income.
State Income Tax
The amount of taxes withheld should then be deducted from the taxpayer’s income tax at the end of the year. Hopefully, this article helped to explain why no federal income tax was withheld from your paycheck. Union workers, however, may see legal deductions that don’t fall in either of these categories if such deductions are authorized by your collective bargaining agreement. An example of this kind of deduction is a pension payment. Enrollment in, or completion of, the H&R Block Income Tax Course is neither an offer nor a guarantee of employment.
You can elect to have federal income tax withheld from your unemployment compensation benefits, much like income tax would be withheld from a regular paycheck. Less than one-third of tax filers opted to itemize deductions on their federal income tax returns in 2016, but virtually all who itemized claimed a deduction for state and local taxes paid. High-income households are more likely than low- or moderate-income households to benefit from the SALT deduction.
Federal Withholding Tax vs. State Withholding Tax: An Overview
Withholding of tax on wages includes income tax, social security and medicare, and a few taxes in some states. Certain minimum amounts of wage income are not subject to income tax withholding.
Tax rates and withholding tables apply separately at the federal, most state, and some local levels. The amount to be withheld is based on both the amount wages paid on any paycheck and the period covered by the paycheck. Federal and some state withholding amounts are at graduated rates, so higher wages have higher withholding percentages. Withholdings in excess of tax so determined are refunded.
All tax situations are different and not everyone gets a refund. Fees apply if you have us file an amended return. The IRS allows taxpayers to amend returns from the previous three tax years to claim additional refunds to which they are entitled.
In many cases, the rates charged to non-residents are lower than to residents, considering that commuters generally use less of these services than do residents. While claiming one allowance on your W-4 means your employer will take less money out of your paycheck for federal taxes, it does not impact how much taxes you’ll actually owe. Depending on your income and any deductions or credits that apply to you, you may receive a tax refund or have to pay a difference. The IRS views unemployment compensation as income, and generally taxes it accordingly.
Instead, it requires that the filer enter specific dollar amounts, and it uses a five-step process that lets you enter personal information, claim dependents and indicate any additional income. These changes mainly apply to anyone adjusting their withholdings and those who got a new job following Jan. 1, 2020. For reference, employees hired before 2020 aren’t required to complete a new W-4. Finally, the tax return you file in April 2021 will contain any adjustments you’ve made to your withholdings in 2020. Only available for returns not prepared by H&R Block.
Their residents who work in neighboring states must file resident tax returns in their home states and non-resident returns in the states where they work. In general, the jurisdiction where money is earned has first claim on the taxes, and so the non-resident return should be completed first. State resident income tax returns generally allow taxpayers to take credit for taxes paid to other jurisdictions, although there may be limitations to such credits. You can use IRS Form 1040 to complete your federal tax requirements.
Do You Have to Pay Income Tax to a Nonresidential State?
The business (as a tax withholding agent) is required to provide BIR Form 2307 (or Form 2306 in certain cases) to the supplier as proof of the withholding. The supplier can then use that form as evidence of payment.