SG&A expenses are typically the costs associated with a company’s overall overhead since they can not be directly traced to the production of a product or service. SG&A includes nearly everything that isn’t included incost of goods sold(COGS). Interest expense is one of the notable expenses not in SG&A and is listed as a separate line item on the income statement.
Simply put, selling and administrative expenses are all the expenses not directly related to the production of a product. That includes the budgets of all non-manufacturing departments such as marketing, accounting, sales, engineering, and so on. General and administrative expenses appear in the income statement immediately below the cost of goods sold.
Selling, general, and administrative expenses also consist of a company’s operating expenses that are not included in the direct costs of production or cost of goods sold. While this is typically synonymous with operating expenses, many times companies list SG&A as a separate line item on the income statement below cost of goods sold, under expenses.
Selling and administrative expenses are typically a huge line item on a company’s income statement. It includes most every expense the company incurs not directly related to the production of its products. Whether a company wants to grow, cut costs, or simply maintain what it’s doing, managers must pay close attention to this figure and all its component parts. Managing this section of the income statement is a crucial component to running a successful business.
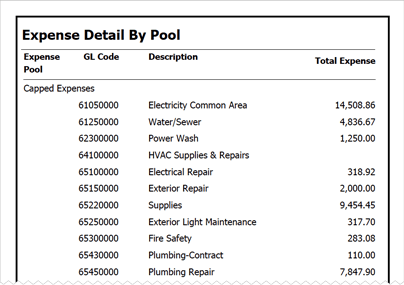
G&A expenses include rent, utilities, insurance, legal fees, and certain salaries. Typically, any cost that does not link to the production or the selling process and is not part of research and development is classified as a general and administrative expense. As a result, general and administrative expenses do not fall under cost of goods sold and are not inventory. General and administrative expenses are also typically fixed costs in nature, as they would stay the same regardless of the level of sales that occur.
General and administrative (G&A) expenses are incurred in the day-to-day operations of a business and may not be directly tied to a specific function or department within the company. General expenses pertain to operational overhead expenses that impact the entire business. Administrative expenses are expenses that cannot be directly tied to a specific function within the company such as manufacturing, production, or sales.
General costs such as office supplies, telephone bills, and postage are considered to be administrative expenses. Compensation for employees who provide overall support for the company that is not tied to a specific department is also considered an administrative expense.
General And Administrative Expense (G&A)
The company is losing money every month, but the sales are through the roof. After looking at the expenses, management found out that general and admin expenses were three times what selling expenses were.
In times of financial difficulty, operating expenses can become an important focus of management when implementing cost controls. Operating expenses include costs that are incurred even when no sales are generated, such as advertising costs, rent, interest payments on debt, and administrative salaries. But typically, selling, general and administrative expenses represent the same costs as operating expenses. Typically, the operating expenses and SG&A of a company represent the same costs – those independent of and not included in cost of goods sold.
Not all general and administrative expenses are grouped as one line item. For example, fees and interest may be classified as their own line item when deducting expenses to arrive at net income. Administrative expenses are the expenses which are not attributable to direct production or delivery of the products or services of a company.
- While this is typically synonymous with operating expenses, many times companies list SG&A as a separate line item on the income statement below cost of goods sold, under expenses.
- Selling, general, and administrative expenses also consist of a company’s operating expenses that are not included in the direct costs of production or cost of goods sold.
Management can then adjust the admin expenses and staff personnel to lower the general and admin expenses. However, some companies may report selling expenses as a separate line item, in which case the SG&A is changed to G&A. Like operating expenses, administrative expenses are incurred regardless of the number of sales being generated by the company.
The decision to list SG&A and operating expenses separately on the income statement is up to the company’s management. Some companies may prefer more discretion when reporting employee salaries, pensions, insurance, and marketing costs. As a result, an aggregate total of all non-production expenses is compiled and reported as a single line item titled SG&A.
General and administrative (G&A) expenses are listed below cost of goods sold (COGS) on a company’s income statement. The top section of an income statement always displays the company’s revenues for the given accounting period.
Because administrative expenses do not directly contribute to sales or production, there is a strong incentive for management to lower a company’s general and administrative expenses. However, since these costs are typically fixed, there is a limited ability to reduce them.
But sometimes, SG&A is listed as a subcategory of operating expenses on the income statement. In other words, administrative expenses are a subset of operating expenses and can be listed as G&A to separate selling expenses from the general administrative costs of running the company. Of course, if a company includes its selling costs in administrative expenses, it’ll be listed under SG&A on the income statement. It all depends on how the company wants to break out their operating expenses.
What are general expenses?
Management and general expenses are the costs associated with the overall administration of the organization. It is an overall expense of doing business. Other common management and general expenses include accounting, legal, general liability insurance, investment expenses, office management, and board meetings.
How Do Operating Expenses Affect Profit?
COGS is deducted from the net revenue figure to determine the gross margin. The general and administrative expenses are then deducted from the gross margin to arrive at net income.
Understanding General and Administrative Expenses (G&A)
General and administrative expenses typically refer to expenses that are still incurred by a company, regardless of whether the company produces or sells anything. This type of expense is shown on the income statement, typically belowcost of goods sold (COGS) and lumped with selling expenses, forming a selling, general and administrative expense line item. Information on this type of expense is especially useful when calculating a company’s fixed costs. Dividing operating expenses into selling and general and administrative expenses helps management plan its strategy and run the business more effectively.
These expenses include salaries of senior employees, accounting and finance cost, HR expenses etc. These are non-operating expenses necessary to maintain the basic operations of a company. These expenses are also called central expenses and are vital to maintain proper functioning of a company and increase efficiency of operations. In other words, these expenses are somewhat fixed and the company needs to incur regardless of the level of sales.
Operating expenses and selling, general and administrative expenses (SG&A) are both types of costs involved in running a company, and significant in determining its financial well-being. While generally synonymous, they each can be listed separately on the corporate income statement.