Assets are also grouped according to either their life span or liquidity – the speed at which they can be converted into cash. Current assets are items that are completely consumed, sold, or converted into cash in 12 months or less. Examples of current assets include accounts receivable and prepaid expenses. Asset accounts, for example, can be divided into cash, supplies, equipment, deferred expenses and more.
This situation typically arises when a company sells to a customer on account. Selling on account means that the company provides goods or services to a customer not for cash, but instead for the right to collect cash in the future. -Use the Trial Balance section to prove the equality of debits and credits in the general ledger. -Use the Adjustments section to enter changes in account balances that are needed to present an accurate and complete picture of the financial affairs of the business. -Use the Adjusted Trial Balance section to verify the equality of debits and credits after the adjustments.
This makes sense when you think about it because the company has only three ways of acquiring new assets. As noted earlier, expenses are almost always debited, so we debit Wages Expense, increasing its account balance.
The certificates include Debits and Credits, Adjusting Entries, Financial Statements, Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, Working Capital and Liquidity, and Payroll Accounting. A company’s legal debts or obligations that arise during the course of business operations. Recorded on the balance sheet (right side), include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues and accrued expenses. An alternative method of accounting would be to report revenues and expenses when services are provided, regardless of when cash is received or paid. This produces a better measure of the profits arising from the company’s activities.
Instead, each revenue and expense is accumulated in a separate account, making it easier to identify the amount to report for each item on the income statement. Because revenue and expense accounts are subcategories of Retained Earnings, they are affected by debits and credits in the same way as all stockholders’ equity accounts. Notice that the income statement reports the financial effects of business activities that occurred during just the current period. They relate only to the current period and do not have a lingering financial impact beyond the end of the current period.
“Revenues” and “Expenses” are subcategories within retained earnings. They are shown this way because revenues and expenses eventually flow into Retained Earnings, but they aren’t initially recorded there.
Inventories are reported at cost or on lower of cost or market basis. Just like the accounting equation, the assets must always equal the sum of the liabilities and owner’s equity.
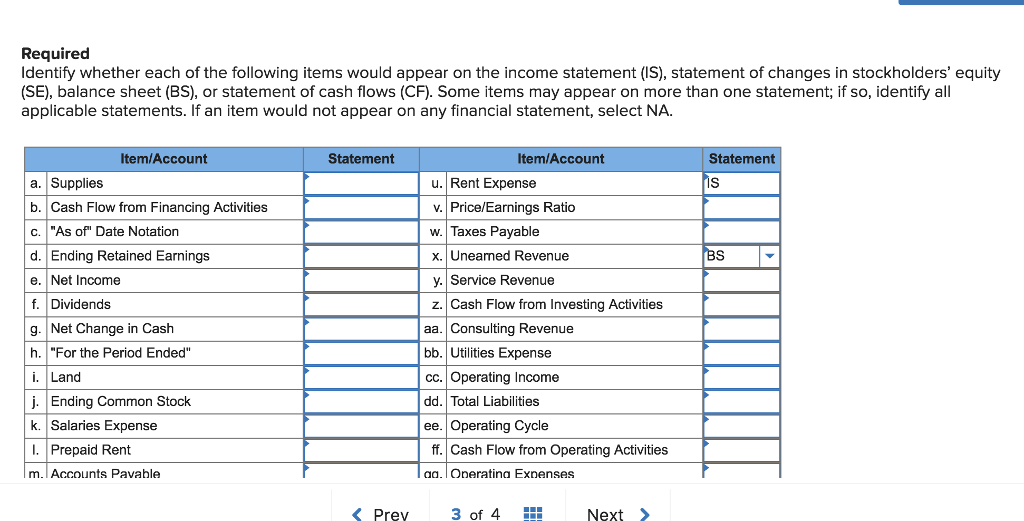
Rent expense
Thus current recievable balances are reduced by allowances for estimated uncollectable accounts. Investments in debt and equity are securites are reported , in most cases, at current market value.
An example is when the company receives cash for gift cards that customers use to pay for goods in the future. This obligation is a liability called “Unearned Revenue”, and it is recorded on the balance sheet equal in amount to the cash received for the gift card. Cash is to be received in a period after goods or services are provided.
What is rent expense classified as?
(Rent that has been paid in advance is shown on the balance sheet in the current asset account Prepaid Rent.) Depending upon the use of the space, Rent Expense could appear on the income statement as part of administrative expenses or selling expenses.
Notice that it is the timing of the underlying business activities, not the cash payments, that dictates when expenses are recognized. Cash payments may occur at the same time as, before, or after the related expenses are incurred to generate revenue. Cash is paid at the same time that the expense is incurred to generate revenue. Although this isn’t as common in business as in your personal life, expenses are sometimes paid for in the period that they arise. In other words, the benefits of incurring the cost are entirely used up in the current accounting period.
At the end of the accounting year the balances will be transferred to the owner’s capital account or to a corporation’s retained earnings account. Whenever cash is received, the asset account Cash is debited and another account will need to be credited. Since the service was performed at the same time as the cash was received, the revenue account Service Revenues is credited, thus increasing its account balance. Revenues and gains are recorded in accounts such as Sales, Service Revenues, Interest Revenues (or Interest Income), and Gain on Sale of Assets. These accounts normally have credit balances that are increased with a credit entry.
Cash is paid before the expense is incurred to generate revenue. It is common for businesses to pay for something that provides benefits only in future periods. Although rent is paid and supplies are purchased before they are used, many costs are paid after receiving and using goods or services. If the rented space was used to manufacture goods, the rent would be part of the cost of the products produced.
Their role is to define how your company’s money is spent or received. Each category can be further broken down into several categories. Generally, expenses are debited to a specific expense account and the normal balance of an expense account is a debit balance. We now offer eight Certificates of Achievement for Introductory Accounting and Bookkeeping.
Common stock, dividends and retained earnings are all examples of equity. An item on the balance sheet that reports the value of a company’s assets that are cash or can be converted into cash immediately. Examples of cash and equivalents are bank accounts, marketable securities and Treasury bills.
All companies expect to receive cash in exchange for providing goods and services, but the timing of cash receipts does not dictate when revenues are recognized. Instead, the key factor in determining when to recognize revenue is whether the company has provided goods or services to customers during the accounting period.
- The best way to ensure your accounts are “in balance” is to prepare a trial balance.
- A trial balance is an internal report used to determine whether total debits equal total credits.
Another way people describe this difference is that the balance sheet takes stock of what exists at a point in time whereas the income statement depicts a flow of what happened over a period of time. There are five main types of accounts in accounting, namely assets, liabilities, equity, revenue and expenses.
The best way to ensure your accounts are “in balance” is to prepare a trial balance. A trial balance is an internal report used to determine whether total debits equal total credits. Typically, a trial balance lists every account name in one column (usually in the order of assets, liabilities, stockholders’ equity, revenues, and expenses). The ending balances obtained from the ledgers (T-accounts) are listed in the appropriate debit or credit column. A list of all accounts with their balances to provide a check on the equality of the debits and credits.
Since your company did not yet pay its employees, the Cash account is not credited, instead, the credit is recorded in the liability account Wages Payable. Since cash was paid out, the asset account Cash is credited and another account needs to be debited. Because the rent payment will be used up in the current period (the month of June) it is considered to be an expense, and Rent Expense is debited.
Rent Expense Definition
If the payment was made on June 1 for a future month (for example, July) the debit would go to the asset account Prepaid Rent. Expenses normally have debit balances that are increased with a debit entry. Since expenses are usually increasing, think “debit” when expenses are incurred. The equity account defines how much your business is currently worth. It’s the residual interest in your company’s assets after deducting liabilities.
This is a key distinction between the income statement and the balance sheet. Balance sheet accounts are considered permanent, whereas income statement accounts are considered temporary.
The Income Statement
Cash is received in the same period the goods or services are provided. Cash is received in a period before goods or services are provided.
Rent Expense is Which Type of Account?
Because most companies use credit for their transactions, cash basis accounting is not likely to correspond to business activities that occur during a given period. Net income (the “bottom line”) is the result after all revenues and expenses have been accounted for. The income statement reflects a company’s performance over a period of time. This is in contrast to the balance sheet, which represents a single moment in time.
What appears on an income statement quizlet?
Under accounting guidelines, rent expense belongs to the “selling, general and administrative accounts” category. Other SG&A items include charges as diverse as litigation, office supplies, money a business pays to settle regulatory liabilities, salaries, insurance and depreciation.
Extend the amounts from the Adjusted Trial Balance section to the Income Statement and Balance Sheet sections. -Use the Income Statement and Balance Sheet sections to prepare the financial statements. “Temporary accounts” (or “nominal accounts”) include all of the revenue accounts, expense accounts, the owner’s drawing account, and the income summary account. Generally speaking, the balances in temporary accounts increase throughout the accounting year.
The Income Statement reports the financial effects of business activities that occurred during just the current period. Such timing differences between financial accounting and tax accounting create temporary differences. For example, rent or other revenue collected in advance, estimated expenses, and deferred tax liabilities and assets may create timing differences. Also, there are events, usually one time, which create “permanent differences,” such as GAAP, which recognizes as an expense an item that the IRS will not allow to be deducted. Incorporated businesses are required to include balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements in financial reports to shareholders and tax and regulatory authorities.
The “rule of accrual” is that financial effects of business activities are measured and reported when the activities actually occur. Revenues are recognized when they are earned and expenses when they are incurred. Reports revenues when cash is received and expenses when cash is paid; not allowed under GAAP. An example is when you simply look at your bank account balance to gauge your financial performance.