For example, the depreciation expense is based on the original cost of the asset being depreciated and not on the current replacement cost. Revenue is only increased when receivables are converted into cash inflows through the collection. Revenue represents the total income of a company before deducting expenses. Companies looking to increase profits want to increase their receivables by selling their goods or services. Typically, companies practice accrual-based accounting, wherein they add the balance of accounts receivable to total revenue when building the balance sheet, even if the cash hasn’t been collected yet.
If a company does not pay cash immediately, you cannot credit Cash. But because the company owes someone the money for its purchase, we say it has an obligation or liability to pay. Most accounts involved with obligations have the word “payable” in their name, and one of the most frequently used accounts is Accounts Payable. Because Direct Delivery received $10, it must debit the account Cash. The second account will be Service Revenues, an income statement account.
The financial statements also reflect the basic accounting principle known as the cost principle. This means assets are shown on the balance sheet at their original cost or less and not at their current value.
There are five main types of accounts in accounting, namely assets, liabilities, equity, revenue and expenses. Their role is to define how your company’s money is spent or received. Each category can be further broken down into several categories.
Debits and Credits Outline
The reason Service Revenues is credited is because Direct Delivery must report that it earned $10 (not because it received $10). Recording revenues when they are earned results from a basic accounting principle known as the revenue recognition principle. Asset accounts, for example, can be divided into cash, supplies, equipment, deferred expenses and more. Service Revenue is income a company receives for performing a requested activity. The charges for such revenue are recorded under the accrual method of accounting.
Accounts payable is a liability since it’s money owed to creditors and is listed under current liabilities on the balance sheet. Current liabilities are short-term liabilities of a company, typically less than 90 days. Now that you know what temporary accounts and permanent accounts are, let’s look at the difference between the two.
Asset, liability, and most owner/stockholder equity accounts are referred to as “permanent accounts” (or “real accounts”). Permanent accounts are not closed at the end of the accounting year; their balances are automatically carried forward to the next accounting year. Accounts payable is a liability account and has a default Credit side.
The most likely liability account involved in business obligations is Accounts Payable. Revenues and gains are recorded in accounts such as Sales, Service Revenues, Interest Revenues (or Interest Income), and Gain on Sale of Assets.
The purpose of temporary accounts is to show how any revenues, expenses, or withdrawals (which are usually called draws) have affected the owner’s equity accounts. The accounts that fall into the temporary account classification are revenue, expense, and drawing accounts. Permanent accounts, which are also called real accounts, are company accounts whose balances are carried over from one accounting period to another. Permanent accounts are the accounts that are seen on the company’s balance sheet and represent the actual worth of the company at a specific point in time.
No, accounts payable are balance account what go on the balance sheet as a liabilities. Accounts payable could be written off as expenses ( for example, reserves) as a result could be recognized in expenses of the period. Using depreciation, a business expenses a portion of the asset’s value over each year of its useful life, instead of allocating the entire expense to the year in which the asset is purchased. This means that each year that the equipment or machinery is put to use, the cost associated with using up the asset is recorded. The rate at which a company chooses to depreciate its assets may result in a book value that differs from the current market value of the assets.
- For one, it keeps the balance sheet and the accounting equation in balance.
- Notice that the year-to-date net income (bottom line of the income statement) increased Stockholders’ Equity by the same amount, $180.
At the end of the accounting year the balances will be transferred to the owner’s capital account or to a corporation’s retained earnings account. From an accounting standpoint, the company would recognize $50 in revenue on itsincome statementand $50 in accrued revenue as an asset on its balance sheet.
When an asset is impaired, its fair value decreases, which will lead to an adjustment of book value on the balance sheet. If the carrying amount exceeds the recoverable amount, an impairment expense amounting to the difference is recognized in the period. If the carrying amount is less than the recoverable amount, no impairment is recognized. Expenses are matched with revenues or with the period of time shown in the heading of the income statement, not in the period when the expenses were paid. This reflects the basic accounting principle known as the matching principle.
This has the effect of overstating net income in financial statements. Accounts payable are not to be confused with accounts receivable. Accounts receivablesare money owed to the company from its customers. As a result, accounts receivable are assets since eventually, they will be converted to cash when the customer pays the company in exchange for the goods or services provided. Accounts payable are the opposite of accounts receivable, which are current assets that include money owed to the company.
Under the accrual basis of accounting, the Service Revenues account reports the fees earned by a company during the time period indicated in the heading of the income statement. Service Revenues include work completed whether or not it was billed. Service Revenues is an operating revenue account and will appear at the beginning of the company’s income statement. We now offer eight Certificates of Achievement for Introductory Accounting and Bookkeeping. The certificates include Debits and Credits, Adjusting Entries, Financial Statements, Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, Working Capital and Liquidity, and Payroll Accounting.
When the company collects the $50, the cash account on the income statement increases, the accrued revenue account decreases, and the $50 on the income statement will remain unchanged. Revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods or services related to the company’s primary operations. Profit, typically called net profitor the bottom line, is the amount of income that remains after accounting for all expenses, debts, additional income streams and operating costs.
Notice that the year-to-date net income (bottom line of the income statement) increased Stockholders’ Equity by the same amount, $180. This connection between the income statement and balance sheet is important. For one, it keeps the balance sheet and the accounting equation in balance. Secondly, it demonstrates that revenues will cause the stockholders’ equity to increase and expenses will cause stockholders’ equity to decrease. This will mean the revenue and expense accounts will start the new year with zero balances—allowing the company “to keep score” for the new year.
Permanent and Temporary Accounts
These accounts normally have credit balances that are increased with a credit entry. Companies must maintain the timeliness and accuracy of their accounts payable process. Delayed accounts payable recording can under-represent the total liabilities.
Accounts payable is a promise made by company to pay for goods/services later. The credit balance in Accounts payable indicates the sum of money the company owes to suppliers or vendors.
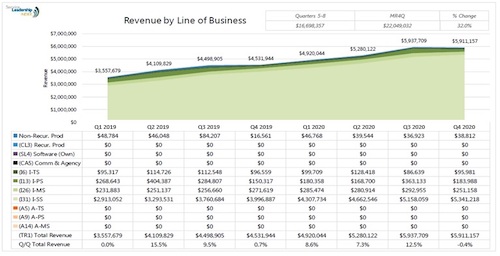
Service revenue
Accrual accounting records the dollar amounts for a charge when a transaction occurs, not when the cash is actually exchanged. This means all fees for services performed to date can be included in an income statement, even if not all the bills have been sent out to clients yet. Service revenue is the income a company generates from providing a service. The amount is displayed at the top of an income statement and is added to the revenue from product earnings to show a company’s total revenue during a specific time period. In a double entry system of accounting, service revenue bookkeeping entries reflect an increase in a company’s asset account.
Temporary accounts accrue balances only for a single accounting period. At the end of the accounting period, those balances are transferred to either the owner’s capital account or the retained earnings account. Which account the balances are transferred to depends on the type of business that is operated. If a company does not pay cash right away for an expense or for an asset, you cannot credit Cash. Because the company owes someone the money for its purchase, we say it has an obligation or liability to pay.
One way these accounts are classified is as temporary or permanent accounts. Temporary accounts are company accounts whose balances are not carried over from one accounting period to another, but are closed, or transferred, to a permanent account. For one, they appear on completely different parts of a company’s financial statements. Assets are listed on the balance sheet, and revenue is shown on a company’s income statement.
Is service revenue asset or liability?
Service revenue is the sales reported by a business that relate to services provided to its customers. This revenue has usually already been billed, but it may be recognized even if unbilled, as long as the revenue has been earned.
Service revenue appears at the top of an income statement, and is separated but added to the product sales for a revenue total. “Temporary accounts” (or “nominal accounts”) include all of the revenue accounts, expense accounts, the owner’s drawing account, and the income summary account. Generally speaking, the balances in temporary accounts increase throughout the accounting year.