
The beginning inventory is especially important when it comes to calculating the cost of goods sold. To calculate the cost of goods sold, you start out with the beginning inventory, add any purchases made during the period, and subtract the ending inventory. This information appears on the income statement of the accounting period for which purchases are being measured.
This means that each year that the equipment or machinery is put to use, the cost associated with using up the asset is recorded. The rate at which a company chooses to depreciate its assets may result in a book value that differs from the current market value of the assets. DefinitionThe average payment period (APP) is defined as the number of days a company takes to pay off credit purchases. It is calculated as accounts payable / (total annual purchases / 360). As the average payment period increases, cash should increase as well, but working capital remains the same.
Financing cash flow involves proceeds from sale or purchase of equity and debt securities. The cost for capital assets may include transportation costs, installation costs, and insurance costs related to the purchased asset. If a firm purchased machinery for $500,000 and incurred transportation expenses of $10,000 and installation costs of $7,500, the cost of the machinery will be recognized at $517,500. Keep the unsatisfactory merchandise, and seek an allowance from the seller.
He also needs to debit accounts payable to reduce the amount owed the supplier by the amount that was returned. Operating expenses are expenses incurred during regular business, such as general and administrative expenses, research and development, and the cost of goods sold. Operating expenses are much easier to understand conceptually than capital expenses since they are part of the day-to-day operations. All operating expenses are recorded on a company’s income statement as expenses in the period when they were incurred. The first section of an income statement reports a company’s sales revenue, purchase discounts, sales returns and cost of goods sold.
This is done by recording the amount of the allowance in the purchases returns and allowances account. Purchases returns and allowances is a contra account to purchases.
An allowance is a reduction in price granted by the seller to the buyer. The original purchase must be reduced on the books by the amount of the allowance.
Purchase credit journal entry is recorded in the books of accounts of the company when the goods are purchased by the company on credit from the third party (vendor). Capital expenditures—any outlay made by your company to procure fixed assets, such as the long-term use of machinery or property—are assumed to be consumed over their useful life and are expensed gradually, via their depreciation value. Company B’s brand-new research facility, for instance, would be a capital expenditure. The costs of running the machinery in it, on the other hand, would be revenue expenditures.
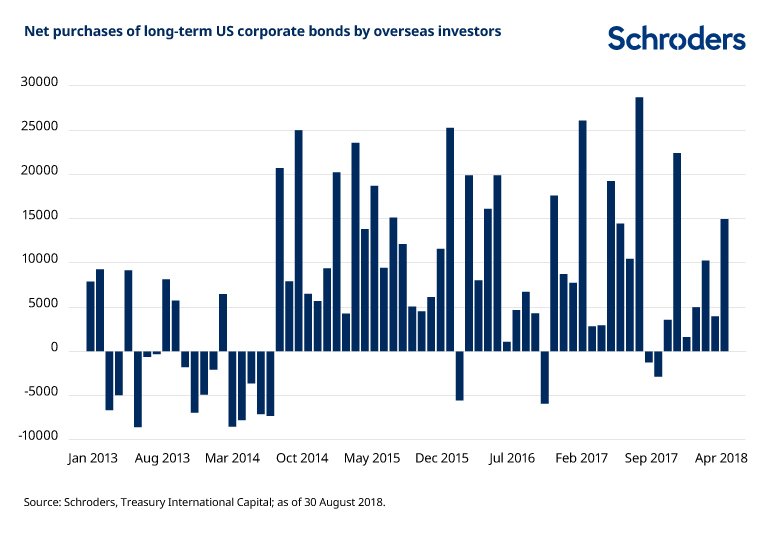
How do you calculate net purchases?
Net purchases is defined as the gross amount of purchases made, less deductions for purchase discounts, returns, and allowances.
A common depreciation method is the straight-line method, in which the annual depreciation expense is the same each year. The depreciation accounting entries are to debit depreciation expense and credit accumulated depreciation, which reduces the book value of fixed assets on the balance sheet.
Accountants must make specific journal entries to record purchase discounts. When a buyer pays the bill within the discount period, accountants debit cash and credit accounts receivable. Another part of the entry debits purchase discounts and credits accounts receivable for the discount taken by the buyer.
For businesses, a capital asset is an asset with a useful life longer than a year that is not intended for sale in the regular course of the business’s operation. For example, if one company buys a computer to use in its office, the computer is a capital asset. If another company buys the same computer to sell, it is considered inventory. When adding a COGS journal entry, you will debit your COGS Expense account and credit your Purchases and Inventory accounts.
- Using depreciation, a business expenses a portion of the asset’s value over each year of its useful life, instead of allocating the entire expense to the year in which the asset is purchased.
This information directly affects a company’s gross and operating profit. A purchase discount is a small percentage discount a company offers to a buyer to induce early payment of goods sold on account. Depreciation is the periodic allocation of a fixed asset’s costs over its useful life, which is substantially longer than a year.
Most companies try to decrease the average payment period to keep their larger suppliers happy and possibly take advantage of trade discounts. Purchases will normally have a debit balance since it represents additions to the inventory, an asset. The contra account purchases returns and allowances will have a credit balance to offset it. Bill uses the purchases returns and allowances account because he likes to keep tabs on the amount as a percentage of purchases.
This figure, otherwise called total purchases, serves as the numerator in the accounts payable turnover ratio. When a business purchases capital assets, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) considers the purchase a capital expense. In most cases, businesses can deduct expenses incurred during a tax year from their revenue collected during the same tax year, and report the difference as their business income. However, most capital expenses cannot be claimed in the year of purchase, but instead must be capitalized as an asset and written off to expense incrementally over a number of years. Capital assets are significant pieces of property such as homes, cars, investment properties, stocks, bonds, and even collectibles or art.
Revenue accounts carry a natural credit balance; purchase discounts has a debit balance as a contra account. On the income statement, purchase discounts goes just below the sales revenue account. Accounts receivable is a current asset included on the company’s balance sheet. Capital assets are assets that are used in a company’s business operations to generate revenue over the course of more than one year.
Capital expenses are recorded as assets on a company’s balance sheet rather than as expenses on the income statement. The asset is then depreciated over the total life of the asset, with a period depreciation expense charged to the company’s income statement, normally monthly. Accumulated depreciation is recorded on the company’s balance sheet as the summation of all depreciation expenses, and it reduces the value of the asset over the life of that asset. A purchase return occurs when a buyer returns merchandise that it had purchased from a supplier. Since the return of purchased merchandise is time consuming and costly, under the periodic inventory system there will be an account Purchases Returns.
Net income is sales minus expenses, which include cost of goods sold, general and administrative expenses, interest and taxes. The net income becomes negative, meaning it is a loss, when expenses exceed sales. Total cash flow is the sum of operating, investing and financing cash flows. Operating cash flow is usually different from net income because of adjustments for non-cash transactions. Investing cash flow usually consists of fixed asset transactions, such as the acquisition or sale of a manufacturing facility.
How Are Net Credit Purchases Calculated?
Using depreciation, a business expenses a portion of the asset’s value over each year of its useful life, instead of allocating the entire expense to the year in which the asset is purchased. The purpose of depreciating an asset over time is to align the cost of the asset to the same year as the revenue generated by the asset, in line with the matching principle of U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
How to Evaluate a Company’s Balance Sheet
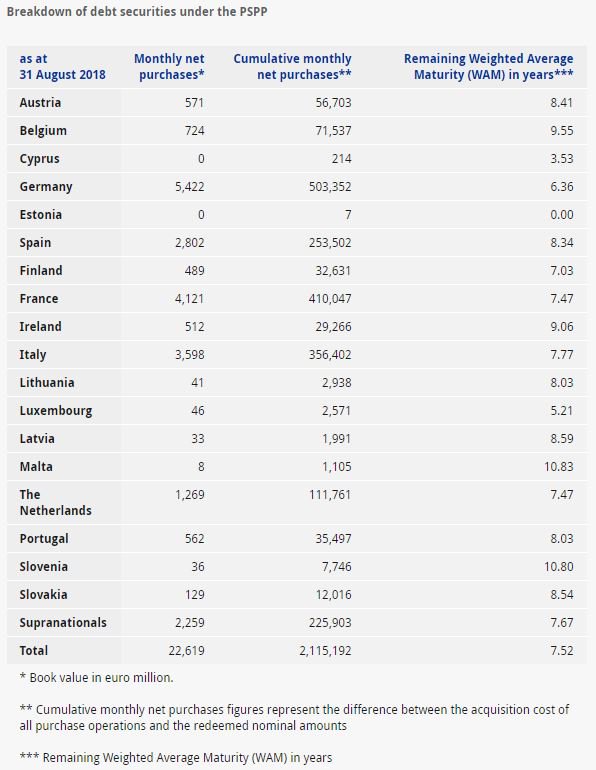
This allows the company’s management to see the magnitude of the returns that occurred. The accounts payable turnover ratio treats net credit purchases as equal to the cost of goods sold (COGS) plus ending inventory, less beginning inventory.
Net purchases
The debit to accounts payable reduces the amount Bill owes the supplier by the amount of the allowance. The credit to purchases returns and allowances reduces the value of the defective bikes in the purchases account. These two types of expenses are treated differently when it comes to accounting and financial statements. However, a company can sometimes choose whether an expense will be an operating or capital expense, for example, whether a needed asset is leased or bought. Add your ending inventory to the cost of goods sold and then subtract the amount of purchases you made in the accounting period.
For example, if a small business has a $5,000 computer on its books, the annual depreciation expense over its estimated five-year useful life is $5,000 divided by 5, or $1,000. This expense will reduce net income, but it will be added back to operating cash flow because it is a non-cash expense. Therefore, while net income could be negative, the cash flow would show a gain. Essentially, a capital expenditure represents an investment in the business.