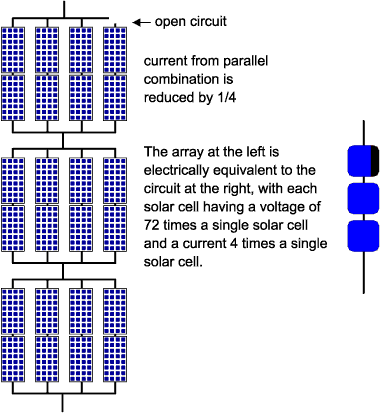
Due to the low voltage of an individual solar cell (typically ca. 0.5V), several cells are wired (also see copper used in PV systems) in series in the manufacture of a “laminate”. The laminate is assembled into a protective weatherproof enclosure, thus making a photovoltaic module or solar panel. In 2012, solar panels available for consumers have an efficiency of up to about 17%, while commercially available panels can go as far as 27%.
The first practical application of photovoltaics was to power orbiting satellites and other spacecraft, but today the majority of photovoltaic modules are used for grid-connected systems for power generation. There is still a smaller market for stand alone systems for remote dwellings, boats, recreational vehicles, electric cars, roadside emergency telephones, remote sensing, and cathodic protection of pipelines. Solar energy systems generally don’t require a lot of maintenance. You only need to keep them relatively clean, so cleaning them a couple of times per year will do the job. If in doubt, you can always rely on specialised cleaning companies, which offer this service from around £25-£35.
Energy Systems
Solar cell efficiencies vary from 6% for amorphous silicon-based solar cells to 44.0% with multiple-junction concentrated photovoltaics. Solar cell energy conversion efficiencies for commercially available photovoltaics are around 14–22%. Concentrated photovoltaics (CPV) may reduce cost by concentrating up to 1,000 suns (through magnifying lens) onto a smaller sized photovoltaic cell.
What does PV or Photovoltaic mean?
However, such concentrated solar power requires sophisticated heat sink designs, otherwise the photovoltaic cell overheats, which reduces its efficiency and life. To further exacerbate the concentrated cooling design, the heat sink must be passive, otherwise the power required for active cooling would reduce the overall efficiency and economy. The Photovoltaic Panel can be used singly, or connected together in parallel and series with other solar panels and modules to produce a larger solar array with a greater current and voltage output. These arrays can the be arranged as panels on a buildings roof or walls, and can often feed the solar electricity directly into a building.
Quantum dot solar cells are quantum dot sensitized DSSCs and are solution processed meaning they are potentially scalable, but currently they peak at 12% efficiency. Perovskite solar cells are a very efficient solar energy converter and have excellent optoelectric properties for photovoltaic purposes, but they are expensive and difficult to manufacture. Financial incentives for photovoltaics, such as feed-in tariffs, have often been offered to electricity consumers to install and operate solar-electric generating systems. Government has sometimes also offered incentives in order to encourage the PV industry to achieve the economies of scale needed to compete where the cost of PV-generated electricity is above the cost from the existing grid. Such policies are implemented to promote national or territorial energy independence, high tech job creation and reduction of carbon dioxide emissions which cause climate change.
Apart from the inverter, the cables also need maintenance to ensure your solar power system runs at maximum efficiency. So, after covering the initial cost of the solar system, you can expect very little spending on maintenance and repair work. You can generate electricity (photovoltaics) or heat (solar thermal).
Most modules (60 or 72 crystalline silicon cells) generate 160 W to 300 W at 36 volts. It is sometimes necessary or desirable to connect the modules partially in parallel rather than all in series. An individual set of modules connected in series is known as a ‘string’.
In some installations a solar micro-inverter is connected at each solar panel. For safety reasons a circuit breaker is provided both on the AC and DC side to enable maintenance. AC output may be connected through an electricity meter into the public grid.
PV
It has been recorded that a group from The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems have created a cell that can reach 44.7% efficiency, which makes scientists’ hopes of reaching the 50% efficiency threshold a lot more feasible. A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is a power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system’s overall performance and include an integrated battery solution, as prices for storage devices are expected to decline. Strictly speaking, a solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS). As PV systems convert light directly into electricity, they are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling.
Market-share for central and string inverters are about 50 percent and 48 percent, respectively, with less than 2 percent for micro-inverters. A grid connected system is connected to a larger independent grid (typically the public electricity grid) and feeds energy directly into the grid. These systems vary in size from residential (2–10 kWp) to solar power stations (up to 10s of MWp). Feeding electricity into the grid requires the transformation of DC into AC by a special, synchronising grid-tie inverter. In kilowatt-sized installations the DC side system voltage is as high as permitted (typically 1000 V except US residential 600 V) to limit ohmic losses.
- Due to the low voltage of an individual solar cell (typically ca. 0.5V), several cells are wired (also see copper used in PV systems) in series in the manufacture of a “laminate”.
- In 2012, solar panels available for consumers have an efficiency of up to about 17%, while commercially available panels can go as far as 27%.
What does PV mean in texting?
Share Tweet + 1 Mail. Photovoltaic (PV) essentially means electricity from the energy of the sun and is derived from the words “photo” with the Greek meaning light and “voltaic” meaning voltage.
With the latest PV technology, cells can also be integrated into the roof tiles themselves. Groups of solar PV cells can be added together to provide increasing levels of power.
What Is Present Value – PV?
As of 2015, the fast-growing global PV market is rapidly approaching the 200 GW mark – about 40 times the installed capacity in 2006. These systems currently contribute about 1 percent to worldwide electricity generation. The International Energy Agency expects solar power to become the world’s largest source of electricity by 2050, with solar photovoltaics and concentrated solar thermal contributing 16% and 11% to the global demand, respectively. A photovoltaic system, or solar PV system is a power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics.
Because organic photovoltaics require very high purity and are relatively reactive they must be encapsulated which vastly increases cost of manufacturing and meaning that they are not feasible for large scale up. Dye-sensitized PVs are similar in efficiency to OPVs but are significantly easier to manufacture. However these dye-sensitized photovoltaics present storage problems because the liquid electrolyte is toxic and can potentially permeate the plastics used in the cell.
Future Value Compared With PV
Due to economies of scale solar panels get less costly as people use and buy more—as manufacturers increase production to meet demand, the cost and price is expected to drop in the years to come. Solar cells produce direct current electricity from sunlight which can be used to power equipment or to recharge a battery.
Nowadays, most PV systems are grid-connected, while stand-alone systems only account for a small portion of the market. Other emerging PV technologies include organic, dye-sensitized, quantum-dot, and Perovskite photovoltaics. OPVs fall into the thin-film category of manufacturing, and typically operate around the 12% efficiency range which is lower than the 12–21% typically seen by silicon based PVs.
Most reliable solar panel manufacturers offer20-25 years warranty. The inverter is usually the only part that needs to be changed after 5-10 years because it is continuously working to convert solar energy into electricity and heat (solar PV vs. solar thermal).
The number of modules in the system determines the total DC watts capable of being generated by the solar array; however, the inverter ultimately governs the amount of AC watts that can be distributed for consumption. For example, a PV system comprising 11 kilowatts DC (kWDC) worth of PV modules, paired with one 10-kilowatt AC (kWAC) inverter, will be limited to the inverter’s output of 10 kW. As of 2014, conversion efficiency for state-of-the-art converters reached more than 98 percent. While string inverters are used in residential to medium-sized commercial PV systems, central inverters cover the large commercial and utility-scale market.
It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and directly convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to change the electric current from DC to AC, as well as mounting, cabling and other electrical accessories. PV systems range from small, roof-top mounted or building-integrated systems with capacities from a few to several tens of kilowatts, to large utility-scale power stations of hundreds of megawatts.