However, Cost Management warns you of the possibility of inadvertently transferring both distributions to the General Ledger. You can transfer your cost distributions to the General Ledger if you have checked the Post Entries to GL check box in the Cost Type Associations Accounting Options window. You have the option of transferring your cost distributions to the General Ledger for either Periodic or perpetual costing, or both. A period can be changed to open only if there are no other open periods. The current period is the open period in the Periodic Costing calendar for the cost type.
How a Perpetual Inventory Method Works
The bad news is the periodic method does do things just a little differently. Business types using the periodic inventory system include companies that sell relatively few inventory units each month such as art galleries and car dealerships.
Under the perpetual system, there are continual updates to either the general ledger or inventory ledger as inventory-related transactions occur. Cost flow assumptions in periodic inventory system are somewhat similar to perpetual inventory methods as far as formulas are concerned. However, the way calculations are carried out is different because, in periodic inventory, there is no continuous record of sales. Hence, the ledger tally accounts for purchases, and transactions are not kept running.
You can choose to create Periodic Costing distributions and send them to the General ledger after a Periodic Costing run. You can also disable the perpetual costing General Ledger transfer, electing instead to produce accounting entries only after a Periodic Costing run. You must set up a perpetual costing method (standard or average or FIFO or LIFO) for each inventory organization that you establish in Oracle Inventory.
Under a periodic review inventory system, the accounting practices are different than with a perpetual review system. To calculate the amount at the end of the year for periodic inventory, the company performs a physical count of stock. Organizations use estimates for mid-year markers, such as monthly and quarterly reports. Accountants do not update the general ledger account inventory when their company purchases goods to be resold.
Before the period can be closed, all cost groups associated with a legal entity must be processed by the acquisition cost processor and the Periodic Cost processor. The Periodic Cost Processor can be run using either the Periodic Average or Incremental LIFO algorithm. You can define different cost types for each and associate them with one appropriate cost method.
Formulas in Perpetual Inventory Method
As a result, businesses can have inventory spread over more than one physical location while maintaining a centralized inventory management system. Properly managing inventory can make or break a business, and having insight into your stock is crucial to success.
Select the Enable Iterative Periodic Average Costing indicator to enable the Iterative Periodic Average Costing (IPAC) processor at the legal entity and cost type level. If you leave this unchecked, then the application uses the standard periodic cost processor. In Periodic Costing, the cost type is associated with the Periodic Costing method. When you run the Periodic Cost processor and choose cost type, you implicitly choose a cost method. Perpetual inventory systems provide the business owner with a record of detailed sale transactions by item, including where, when, and at what price items were sold.
- Oracle Cost Management Periodic Costing methods require the use of cost types and periodic rates cost types (similar to average rates cost type used in average costing for manufacturing).
- Using the Cost Type Associations Accounting Options window, you can set options pertaining to the creation of accounting entries (cost distributions) and posting (transferring) to General Ledger.
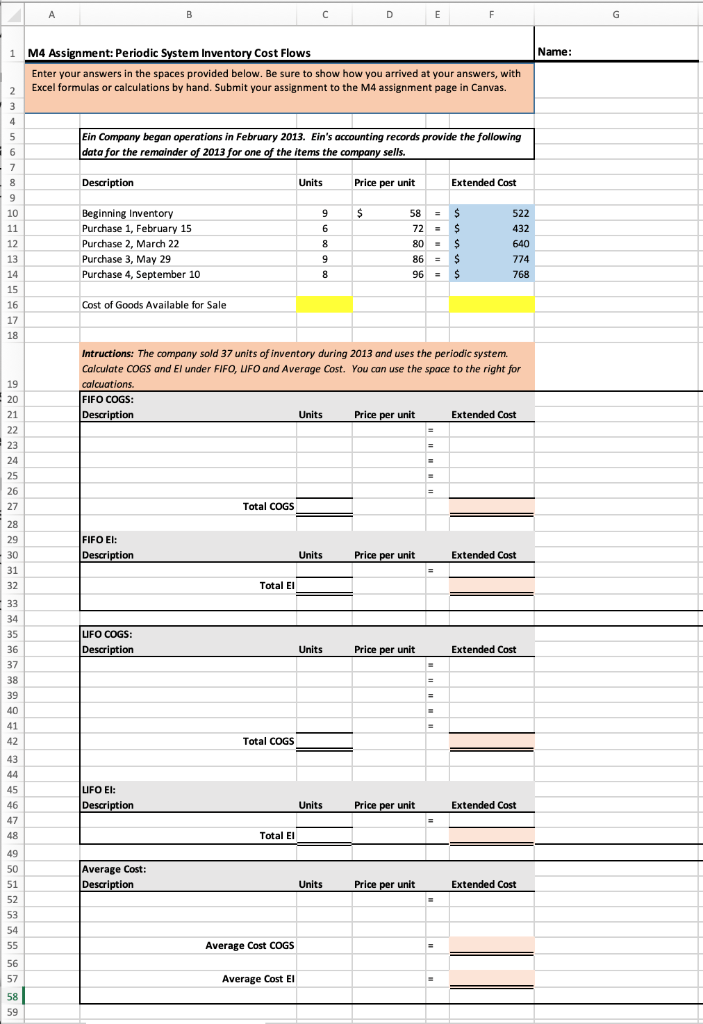
A periodic inventory system is an accounting method in which the cost of goods sold is determined periodically, usually annually and typically not more frequently than quarterly. This differs from a perpetual inventory system in which the cost of goods sold is determined as necessary or in some cases continually. LIFO means last-in, first-out, and refers to the value that businesses assign to stock when the last items they put into inventory are the first ones sold. The products in the ending inventory are either leftover from the beginning inventory or those the company purchased earlier in the period. LIFO in periodic systems starts its calculations with a physical inventory.
What exactly is the Periodic Inventory Method and How it Works
In a perpetual system, the software is continuously updating the general ledger when there are changes to the inventory. In the periodic system, the software only updates the general ledger when you enter data after taking a physical count. In a perpetual system, the COGS account is current after each sale, even between the traditional accounting periods. In the periodic system, you only perform the COGS during the accounting period.
When you enter a currency other than your ledger currency, the system converts item costs to the selected currency using the End of period rate you choose in the Exchange Rate field. Acquisition costs are the sum of the costs associated with the acquisition of the goods. They include material costs, freight, special charges, and non-recoverable taxes. The acquisition cost processor processes all receipt transactions that take place within a period for a particular cost group and cost type. Periodic Costing lets you cost items from one or more inventory organizations on a periodic basis.
This cost is based on invoice price if the invoice is available; otherwise, the purchase price is used for purchased items. For manufactured items, Periodic Costing is the sum of the actual cost of resources and materials consumed. You are in a country with a fiscal requirement to transact and/or report on inventory costs using one or both Periodic Costing methods.
When you Should Use Periodic Inventory Method
In this example, we also say that the physical inventory counted 590 units of their product at the end of the period, or Jan. 31. We use the same table (inventory card) for this example as in the periodic FIFO example. Between the two accounting systems, there are differences in how you update the accounts and which accounts you need.
What is periodic inventory system example?
Periodic inventory is a system of inventory in which updates are made on a periodic basis. In a periodic inventory system no effort is made to keep up-to-date records of either the inventory or the cost of goods sold. Instead, these amounts are determined only periodically – usually at the end of each year.
Periodic inventory
While the periodic method is acceptable for companies that have minimal inventory items or small businesses, those companies that plan to scale will need to implement a perpetual inventory system. Regardless of the type of inventory control process you choose, decision makers need the right tools in place so they can manage their inventory effectively. NetSuite offers a suite of native tools for tracking inventory in multiple locations, determining reorder points and managing safety stock and cycle counts. Find the right balance between demand and supply across your entire organization with the demand planning and distribution requirements planning features. Cost flow assumptions are inventory costing methods in a periodic system that businesses use to calculate COGS and ending inventory.
Using the Cost Type Associations Accounting Options window, you can set options pertaining to the creation of accounting entries (cost distributions) and posting (transferring) to General Ledger. If you do not Create Accounting Entries, you cannot post to the General Ledger from Periodic Costing, and therefore General Ledger options are unavailable to you. Oracle Cost Management Periodic Costing methods require the use of cost types and periodic rates cost types (similar to average rates cost type used in average costing for manufacturing). Cost types for Periodic Costing must be multi-org and not updatable. Any user defined cost type can be a periodic rates cost type if it is so designated in the Cost Type Association tab of the Org Cost Group/Cost Type Associations window.
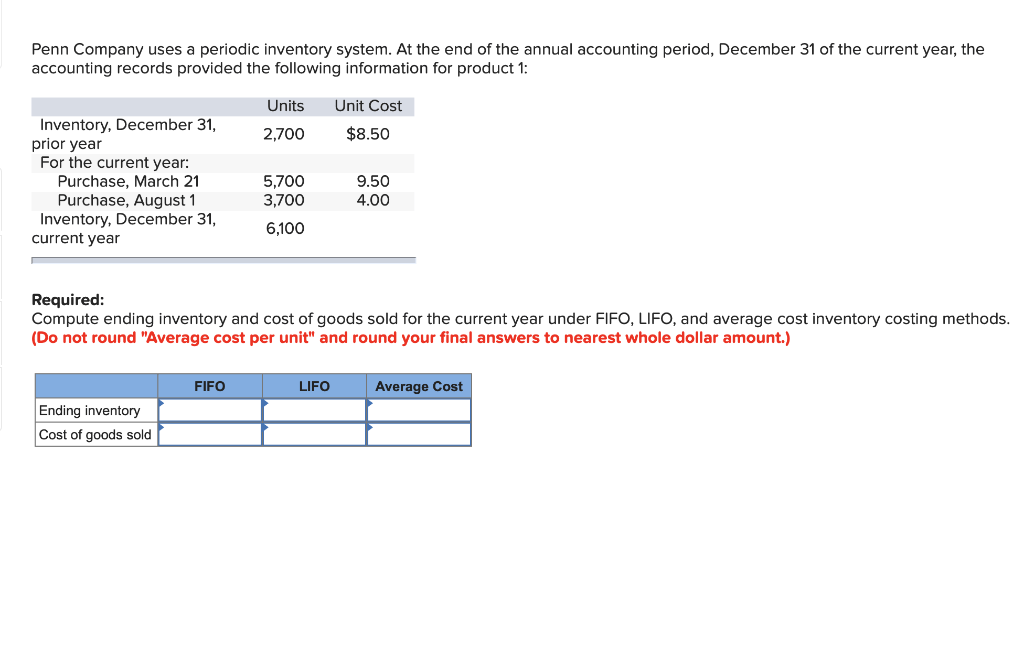
Beginning inventory and purchases are the input that accountants use to calculate the cost of goods available for sale. They then apply this figure to whichever cost flow assumption the business chooses to use, whether FIFO, LIFO or the weighted average. Periodic and perpetual inventory systems are different accounting methods for tracking inventory, although they can work in concert. Overall, the perpetual inventory system is superior because it tracks all data and transactions. However, with a perpetual system, you need to make more decisions to use it successfully.