When are expenses and revenues counted in accrual accounting?
Within Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP Revenue recognition Rules) there are multiple ways to recognize revenues and can look dramatically different depending on the method chosen even when the economic reality is the same. Revenues can be recognized on a sales basis, percentage of completion, cost recoverability and installment. Using the sales basis method, revenue is recognized at the moment the goods or services are transferred to the buyer. In this case, revenue is not recognized even if cash is received before the transaction is complete. The percentage of completion method is used when there is a long-term legally enforceable contract and it is possible to estimate the percentage of project completion, revenues and costs.
The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB), which dictates accounting standards for most companies—especially publicly traded companies—discourages businesses from using the cash model because revenues and expenses are not properly matched. The cash model is acceptable for smaller businesses for which a majority of transactions occur in cash and the use of credit is minimal. For example, a landscape gardener with clients that pay by cash or check could use the cash method to account for her business’ transactions. The revenue recognition principle is a cornerstone of accrual accounting together with the matching principle.
They both determine the accounting period in which revenues and expenses are recognized. According to the principle, revenues are recognized if they are realized or realizable (the seller has collected payment or has reasonable assurance that payment on goods will be collected). Revenues must also be earned (usually occurs when goods are transferred or services rendered), regardless of when cash is received. For companies that don’t follow accrual accounting and use the cash-basis instead, revenue is only recognized when cash is received.
There are different ways to calculate revenue, depending on the accounting method employed. Accrual accounting will include sales made on credit as revenue for goods or services delivered to the customer. It is necessary to check the cash flow statement to assess how efficiently a company collects money owed.Cash accounting, on the other hand, will only count sales as revenue when payment is received.
Differences Between Gross Revenue Reporting vs. Net Revenue Reporting
Earned revenue accounts for goods or services that have been provided or performed, respectively. Developed jointly by the Financial Accounting Standard’s Board (FASB) and International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), ASC 606 provides a framework for businesses to recognize revenue more consistently. The standard’s purpose is to eliminate variations in the way businesses across industries handle accounting for similar transactions. This lack of standardization in financial reporting has made it difficult for investors and other consumers of financial statements to compare results across industries, and even companies within the same industry.
For example, if the customer paid in advance for a service not yet rendered or undelivered goods, this activity leads to a receipt but not revenue. ASC 606 is the new revenue recognition standard that affects all businesses that enter into contracts with customers to transfer goods or services – public, private and non-profit entities. Both public and privately held companies should be ASC 606 compliant now based on the 2017 and 2018 deadlines. IFRS 15 specifies how and when an IFRS reporter will recognise revenue as well as requiring such entities to provide users of financial statements with more informative, relevant disclosures.
By tying revenues and expenses to the completion of sales and other money generating tasks, the income statement will better reflect what happened in terms of what revenue and expense generating activities during the accounting period. A landscaping company completes a one-time landscaping job for their normal fee of $200. The landscaper can recognize the earned revenue immediately upon completion of the job, even if they don’t expect payment from that customer for a few weeks.
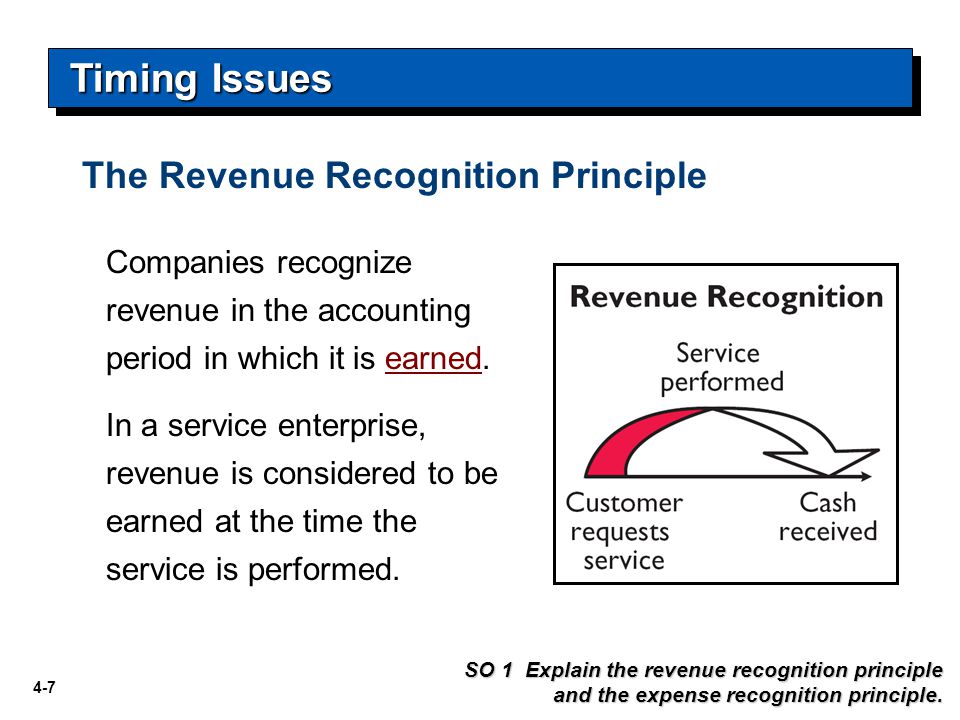
The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) sets the rules for accounting by determining how transactions are recorded in financial statements. The revenue recognition principle has another very important purpose, which is to ensure that the cause-and-effect relationship of expenses and revenue is very clear. By showing revenue when it is earned and connected to the expense that was necessary to earn the revenue, you as a small business owner can much more easily see how profitable certain lines of your business are. The revenue recognition principle, a feature of accrual accounting, requires that revenues are recognized on the income statement in the period when realized and earned—not necessarily when cash is received. Realizable means that goods or services have been received by the customer, but payment for the good or service is expected later.
Often, a business will spend cash on producing their goods before it is sold or will receive cash for good sit has not yet delivered. Without the matching principle and the recognition rules, a business would be forced to record revenues and expenses when it received or paid cash. This could distort a business’s income statement and make it look like they were doing much better or much worse than is actually the case.
- The revenue recognition principle has another very important purpose, which is to ensure that the cause-and-effect relationship of expenses and revenue is very clear.
- The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) sets the rules for accounting by determining how transactions are recorded in financial statements.
Revenue Recognition is the accounting rule that defines revenue as an inflow of assets, not necessarily cash, in exchange for goods or services and requires the revenue to be recognized at the time, but not before, it is earned. You use revenue recognition to create G/L entries for income without generating invoices. The international alternative to GAAP is the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), set by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). This is a list of the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs) and official interpretations, as set out by the IFRS Foundation. It includes accounting standards either developed or adopted by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), the standard-setting body of the IFRS Foundation.
The standard provides a single, principles based five-step model to be applied to all contracts with customers. The accounting principle regarding revenue recognition states that revenues are recognized when they are earned (transfer of value between buyer and seller has occurred) and realized or realizable (collection is reasonably assured). A transfer of value takes place between a buyer and seller when the buyer receives goods in accordance to a sales order approved by the buyer and seller and the seller receives payment or a promise to pay from the buyer for the goods purchased. In order words, for sales where cash was not received, the seller should be confident that the buyer will pay according to the terms of the sale.
What is revenue recognition principle?
revenue recognition principle definition. The accounting guideline requiring that revenues be shown on the income statement in the period in which they are earned, not in the period when the cash is collected. This is part of the accrual basis of accounting (as opposed to the cash basis of accounting).
The cash method of accounting recognizes revenue and expenses when cash is exchanged. For a seller using the cash method, revenue on the sale is not recognized until payment is collected. Just like revenues, expenses are recognized and recorded when cash is paid.
What Is Revenue Recognition?
The old guidance was industry-specific, which created a system of fragmented policies. The updated revenue recognition standard is industry-neutral and, therefore, more transparent.
On May 28, 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) jointly issued Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 606, regarding revenue from contracts with customers. ASC 606 provides a uniform framework for recognizing revenue from contracts with customers.
According to the principle, revenues are recognized when they are realized or realizable, and are earned (usually when goods are transferred or services rendered), no matter when cash is received. In cash accounting – in contrast – revenues are recognized when cash is received no matter when goods or services are sold. The assets produced and sold or services rendered to generate revenue also generate related expenses.
Revenue recognition principle
It allows for improved comparability of financial statements with standardized revenue recognition practices across multiple industries. Before we discuss its value, it’s important to understand what the revenue recognition principle is. In other words, a client can present you with payment, but you may not be able to recognize the entire payment all at once.