Interest Income Accounting
The same amount is also classified as revenue on the income statement. A note receivable is an amount of money a customer or other party owes your company. Your company earns interest on the note receivable to compensate you for extending credit. The amount of interest you earn on the notes receivable in an accounting period, but have yet to be paid, is called interest receivable. The amount of interest you earn regardless of when you receive payment is called interest revenue.
It is a line item and is generally recorded separately from interest expense in the income statement. This income is taxable as per IRS and the ordinary tax rate is applicable for this income. Under the accrual basis of accounting, the Interest Revenues account reports the interest earned by a company during the time period indicated in the heading of the income statement. Interest Revenues account includes interest earned whether or not the interest was received or billed. Interest Revenues are nonoperating revenues or income for companies not in the business of lending money.
Interest Income
When interest is earned on a business account, no receipt or deposit slip is generated. Still, the interest represents earnings for the business and needs to be reflected as such. Additionally, interest added to an account changes its balance, which also must be reflected in the business’s books. An interest expense is the cost incurred by an entity for borrowed funds.
In other words, interest revenue is reported once your business has fulfilled all obligations of a transaction, such as delivering goods to a customer who purchases them on credit. Interest is realizable if you fully expect to receive payment in the future.
Interest expense is a non-operating expense shown on the income statement. It represents interest payable on any borrowings – bonds, loans, convertible debt or lines of credit. It is essentially calculated as the interest rate times the outstanding principal amount of the debt. Interest expense on the income statement represents interest accrued during the period covered by the financial statements, and not the amount of interest paid over that period. While interest expense is tax-deductible for companies, in an individual’s case, it depends on his or her jurisdiction and also on the loan’s purpose.
For example, suppose on June 1 a customer purchases $1,000 worth of equipment on credit and agrees to pay a monthly 1 percent interest charge on the unpaid balance. If the balance remains unpaid on July 1, you’ve earned $10 of interest. Until the interest is paid, or written off as uncollectible, the $10 is included in the interest receivable account. The amount of accrued interest for the party who is receiving payment is a credit to the interest revenue account and a debit to the interest receivable account. The receivable is consequently rolled onto the balance sheet and classified as a short-term asset.
The Income Statement is one of a company’s core financial statements that shows their profit and loss over a period of time. In reality, accounting transactions are recorded by making accounting journal entries. Just like everything else in accounting, there’s a particular way to make an accounting journal entry when recording debits and credits. Under GAAP, revenue is recorded on a company’s books when it’s earned and realizable.
For companies in the business of lending money, Interest Revenues are reported in the operating section of the multiple-step income statement. Asset accounts, for example, can be divided into cash, supplies, equipment, deferred expenses and more.
Revenues and gains are recorded in accounts such as Sales, Service Revenues, Interest Revenues (or Interest Income), and Gain on Sale of Assets. These accounts normally have credit balances that are increased with a credit entry. In this system, only a single notation is made of a transaction; it is usually an entry in a check book or cash journal, indicating the receipt or expenditure of cash.
- We now offer eight Certificates of Achievement for Introductory Accounting and Bookkeeping.
- There is no upper limit to the number of accounts involved in a transaction – but the minimum is no less than two accounts.
A single entry system is only designed to produce an income statement. As an example of interest payable, a business owes $1,000,000 to a lender at a 6% interest rate, and pays interest to the lender every quarter. After one month, the company accrues interest expense of $5,000, which is a debit to the interest expense account and a credit to the interest payable account.
Interest receivable is a balance sheet account that reflects the interest income a business has earned but for which a customer or debtor has yet to pay. This type of account is commonly used by businesses that charge interest on loans and credit lines offered to customers.
After the second month, the company records the same entry, bringing the interest payable account balance to $10,000. After the third month, the company again records this entry, bringing the total balance in the interest payable account to $15,000. It then pays the interest, which brings the balance in the interest payable account to zero. Bookeepers must record all financial transactions that relate to the business’s earnings and expenditures. Most transactions are recorded by posting receipts, checks, deposits and other source documents.
Accrued interest is reported on the income statement as a revenue or expense, depending on whether the company is lending or borrowing. In addition, the portion of revenue or expense yet to be paid or collected is reported on the balance sheet, as an asset or liability. Because accrued interest is expected to be received or paid within one year, it is often classified as a current asset or current liability. The above is an adjusting journal entry that is required at the end of every period.
These accounting terms can tell us how much interest a company earned and how much it expects to earn in the future.
Is interest revenue a current asset?
Interest Revenues are nonoperating revenues or income for companies not in the business of lending money. For companies in the business of lending money, Interest Revenues are reported in the operating section of the multiple-step income statement.
We now offer eight Certificates of Achievement for Introductory Accounting and Bookkeeping. The certificates include Debits and Credits, Adjusting Entries, Financial Statements, Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, Working Capital and Liquidity, and Payroll Accounting. There is no upper limit to the number of accounts involved in a transaction – but the minimum is no less than two accounts.
Thus, the use of debits and credits in a two-column transaction recording format is the most essential of all controls over accounting accuracy. There are five main types of accounts in accounting, namely assets, liabilities, equity, revenue and expenses. Their role is to define how your company’s money is spent or received. Each category can be further broken down into several categories.
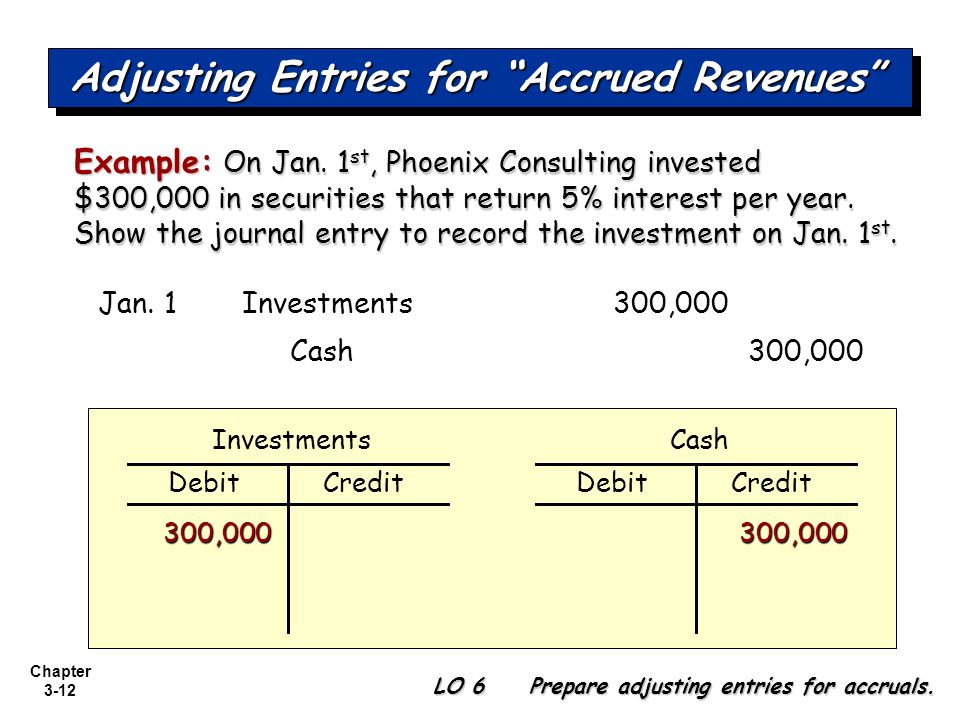
If the company wants updated monthly balances and more accurate monthly financial statements, then the entry should be made every month. Interest Receivable xx.xx Interest Income xx.xx Accrued Interest Receivable (or simply Interest Receivable) is debited to recognize the interest payment to be collected in the future. The entry is made monthly (if more accurate monthly balances are needed) or at the end of the year before the financial statements are prepared. There are some companies who prefer to mention this type of income as penalty income. This is reported within the interest income account in the general ledger.
You can calculate these amounts at the end of your accounting period and report the amounts on your financial statements. The bank is required to send out the details giving how much interest it has paid the owner of the deposit in the bank account. Based on this statement the owner of the deposit gets a clear idea of how much taxable interest income he has earned on the financial assets. So the owner’s business gets the interest payment which is recorded in his income statement as income.