DPS is related to several financial metrics that take into account a firm’s dividend payments, such as the payout ratio and retention ratio. Given the definition of payout ratio as the proportion of earnings paid out as dividends to shareholders, DPS can be calculated by multiplying a firm’s payout ratio by itsearnings per share.
A company’s EPS, equal to net income divided by the number of outstanding shares, is often easily accessible via the firm’s income statement. The retention ratio, meanwhile, refers to the opposite of the payout ratio, as it instead measures the proportion of a firm’s earnings retained and therefore not paid out as dividends.
A growing dividend makes a stock more valuable to investors and may push up the stock price. A liquidating dividend is a situation where the amount of the dividend is greater than the balance in the company’s retained earnings account. In other words, the company is returning part of shareholders’ investment, known as contributed capital, as part of the dividend payment. Apple’s next dividend payment will be US$0.77 per share, and in the last 12 months, the company paid a total of US$3.08 per share.
Stock dividends are sometimes referred to as bonus shares or a bonus issue. Retained earnings are the amount of money a company has left over after all of its obligations have been paid. Retained earnings are typically used for reinvesting in the company, paying dividends, or paying down debt.
What are the four types of dividends?
To record a stock dividend, transfer from retained earnings to the capital stock and additional paid-in capital accounts an amount equal to the fair value of the additional shares issued. The fair value of the additional shares issued is based on their fair market value when the dividend is declared. Property dividend.
This accounting rule can sometimes lead a business to deliberately issue property dividends in order to alter their taxable and/or reported income. Shareholders expect to receive dividend payments on a regular basis for shares that they own. Retained earnings decrease when any type of dividend is declared and company cash is used to pay cash, scrip, and liquidating dividends. Stock dividends involve the issue of company shares to shareholders, and when a property dividend is paid, a company investment decreases. If a company pays stock dividends, the dividends reduce the company’s retained earnings and increase the common stock account.
Companies that fall under the Real Estate Investment Trust and Master Limited Partnership categories are often required to issue a certain percentage of their income as dividends. Investors should always take a close look at the recent performance of a stock before putting money into it. To calculate dividends, find out the company’s dividend per share (DPS), which is the amount paid to every investor for each share of stock they hold. Next, multiply the DPS by the number of shares you hold in the company’s stock to determine approximately what you’re total payout will be. If you’re involved in a dividend reinvestment program, find out how much of your dividends you’re investing so that you know how many shares you own and your calculation remains accurate.
Investors often use dividend yields to determine whether to make certain investments or not. For instance, an investor who’s looking for a steady, regular source of income might invest in a company with a high dividend yield. On the other hand, an investor who’s willing to take a risk for the chance of a major payout might invest in a young company with lots of growth potential. Such companies often keep most of their profits as retained earnings and won’t pay out much in the form of dividends until they are more established. Every share of the $20 company will earn you 2/20 or 10% of your initial investment per year, while every share of the $100 company will earn you just 2/100 or 2% of your initial investment.
Adividendis a method of redistributing a company’s profits to shareholders as a reward for their investment. Companies are not required to issue dividends on common sharesof stock, though many pride themselves on paying consistent or constantly increasing dividends each year. When a company issues a dividend to its shareholders, the dividend can be paid either in cash or by issuing additional shares of stock. The two types of dividends affect a company’sbalance sheet in different ways. After the distribution, the total stockholders’ equity remains the same as it was prior to the distribution.
AccountingTools
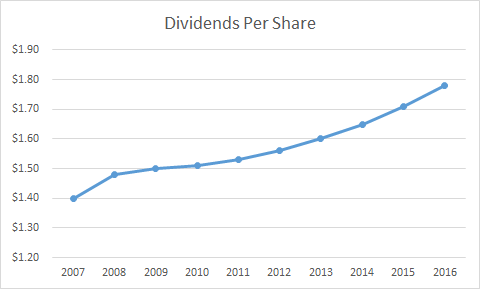
Dividend per share (DPS) is the sum of declared dividends issued by a company for every ordinary share outstanding. The figure is calculated by dividing the total dividends paid out by a business, including interim dividends, over a period of time by the number of outstanding ordinary shares issued. A company’s DPS is often derived using the dividend paid in the most recent quarter, which is also used to calculate the dividend yield. Some companies, like utilities or real estate investment trusts, have a history of increasing dividends over time.
How and Why Do Companies Pay Dividends?
How are property dividends accounted for?
A property dividend is a dividend paid to investors with assets other than cash. For example, a company could send its own products to investors as a dividend. The issuer records the dividend at the fair market value of the assets paid.
- On one hand, it can reinvest this money in the company by expanding its own operations, buying new equipment, and so on.
- When a company makes money, it usually has two general options.
A company may issue a non-monetary dividend to investors, rather than making a cash or stock payment. Record this distribution at the fair market value of the assets distributed. Since the fair market value is likely to vary somewhat from the book value of the assets, the company will likely record the variance as a gain or loss.
Based on the last year’s worth of payments, Apple stock has a trailing yield of around 1.0% on the current share price of $309.51. Dividends are an important source of income to many shareholders, but the health of the business is crucial to maintaining those dividends.
Meanwhile, a growing DPS over time can also be a sign that a company’s management believes that its earnings growth can be sustained. When investors purchase a share in a company, they are doing so for two reasons. Firstly, they hope to enjoy an increase in the value of the purchased shares as the market value increases, and they want to receive a steady income from dividends.
The amounts within the accounts are merely shifted from the earned capital account (Retained Earnings) to the contributed capital accounts (Common Stock and Additional Paid-in Capital). Prior to the distribution, the company had 60,000 shares outstanding.
The difference is the 3,000 additional shares of the stock dividend distribution. The company still has the same total value of assets, so its value does not change at the time a stock distribution occurs. The increase in the number of outstanding shares does not dilute the value of the shares held by the existing shareholders. The market value of the original shares plus the newly issued shares is the same as the market value of the original shares before the stock dividend. For example, assume an investor owns 200 shares with a market value of10 each for a total market value of2,000.
Dividends represent a distribution of a company’s retained earnings to its shareholders. Retained earnings represent the accumulation of all of the earnings that a company has earned and not distributed to its shareholders (owners) since the business started.
She receives 10 shares as a stock dividend from the company. She now has 210 shares with a total market value of2,000. Each share now has a theoretical market value of about9.52.
So we need to investigate whether Apple can afford its dividend, and if the dividend could grow. It’s also important to note that a high dividend yield may not always be a bad sign.
Money paid to investors in this way is called a “dividend”. Calculating the dividend that a shareholder is owed by a company is generally fairly easy; simply multiply the dividend paid per share (or “DPS”) by the number of shares you own. It’s also possible to determine the “dividend yield” (the percentage of your investment that your stock holdings will pay you in dividends) by dividing the DPS by the price per share.
When a company makes money, it usually has two general options. On one hand, it can reinvest this money in the company by expanding its own operations, buying new equipment, and so on. (Money spent this way is called “retained earnings.”) Alternatively, it can use its profits to pay its investors.
Stock dividends do not result in asset changes to the balance sheet but rather affect only the equity side by reallocating part of the retained earnings to the common stock account. By the time a company’s financial statements have been released, the dividend is already paid, and the decrease in retained earnings and cash are already recorded. In other words, investors will not see the liability account entries in the dividend payable account.
How Dividends Are Normally Issued
Dividends are declared by a company’s Board of Directors and paid to shareholders shortly after. While cash dividends have a straightforward effect on the balance sheet, the issuance of stock dividends is slightly more complicated.