These records provide information about a company’s ability—or lack thereof—to generate profit by increasing revenue, reducing costs, or both. The P&L statement is also referred to as the statement of profit and loss, the statement of operations, the statement of financial results, and the income and expense statement.
What is the difference between statement of operations and income statement?
The statement of operations is one of the three primary financial statements used to assess a company’s performance and financial position (the two others being the balance sheet and the cash flow statement). The statement of operations summarizes a company’s revenues and expenses over the entire reporting period.
While most firms do not report their statements in common size format, it is beneficial for analysts to do so to compare two or more companies of differing size or different sectors of the economy. Formatting financial statements in this way reduces bias that can occur and allows for the analysis of a company over various periods.
What is included in an operating statement?
The only real difference between a statement of operation and a statement of income is semantics. Also referred to as a profit and loss statement at times, because it shows the company’s bottom line results for a given period, this report is usually a part of a group of reports prepared by accounting.
One can infer whether a company’s efforts in reducing the cost of sales helped it improve profits over time, or whether the management managed to keep a tab on operating expenses without compromising on profitability. The income statement (also referred to as the profit and loss (P&L) statement) provides an overview of flows of sales, expenses, and net income during the reporting period.
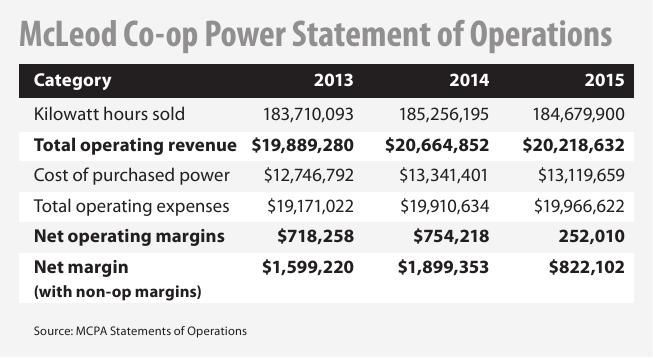
The income statement follows a general form as seen in the example below. It begins with an entry for revenue, known as the top line, and subtracts the costs of doing business, including the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, tax expenses, and interest expenses.
The balance sheet balances out when the assets, liabilities and equity all add up correctly. To ensure that your P&L statement and balance sheet are balanced, review all of the account balances carefully at the end of the reporting period. The P&L statement reveals the company’s realized profits or losses for the specified period of time by comparing total revenues to the company’s total costs and expenses. Over time, it can show a company’s ability to increase its profit, either by reducing costs and expenses, or by increasing sales.
These records provide information about a company’s ability or inability to generate profit by increasing revenue, reducing costs, or both. Some refer to the P&L statement as a statement of profit and loss, income statement, statement of operations, statement of financial results or income, earnings statement or expense statement. A profit and loss statement (P&L), often referred to as the income statement,is afinancial statementthat summarizes the revenues, costs, and expenses incurred during a specific period of time, usually during a fiscal quarter or year.
Sometimes, companies have significant one-time non-operating transactions that can result in a net income or loss completely different from operating income. Creditors may find limited use of income statements as they are more concerned about a company’s future cash flows, instead of its past profitability. Research analysts use the income statement to compare year-on-year and quarter-on-quarter performance.
- The P&L statement includes all of your income for a given period, such as sales, interest and investment gains; and all of your expenses, such as operating costs, fees and costs of goods sold.
- Your company’s P&L is also known as a profit and loss or income statement.
The P&L balances out when the income, expenses and profit or loss add up correctly. The balance sheet includes assets like cash and certain equipment and buildings; current and long-term liabilities such as accounts payable; and owner’s capital.
Why Does a Statement of Operations Matter?
The income statement equation is sales minus expenses and adjustments equals net income. This is why the common size income statement defines all items as a percentage of sales.
The difference, known as the bottom line, is net income, also referred to as profit or earnings. You can find many templates for creating a personal or business P&L statement online for free. The P&L or income statement provides the top and bottom line for a company. The difference, known asthe bottom line, isnet income, also referred to as profit or earnings. Most businesses commonly use “income statement” or “statement of income” when describing this important financial statement.
Companies publish income statements annually, at the end of the company’s fiscal year, and may also publish them on a quarterly basis. Accountants, analysts, and investors study a P&L statement carefully, scrutinizing cash flow and debt financing capabilities. Also known as the profit and loss statement or the statement of revenue and expense, the income statement primarily focuses on the company’s revenues and expenses during a particular period.
Operating expenses include rent, utilities, payroll, employee benefits, and insurance premiums. Operating profit includes all operating costs except interest on debt and the company’s taxes. For example, a company’s revenues may grow, but its expenses might grow at a faster rate.
Operating profitis located further down the income statement and is derived from its predecessor, gross profit. Operating profit or operating income takes gross profit and subtracts all overhead, administrative, and operational expenses.
Gross Profit
Your company’s P&L is also known as a profit and loss or income statement. It and the balance sheet are two of the three main financial reports created at the end of every fiscal year, along with the statement of cash flows. The P&L statement includes all of your income for a given period, such as sales, interest and investment gains; and all of your expenses, such as operating costs, fees and costs of goods sold.
As we shall shortly see in the following example, this segregation helps in identifying how the income and profitability are moving/changing from one level to the other. For instance, high gross profit but lower operating income indicates higher expenses, while higher pre-tax profit and lower post-tax profit indicates loss of earnings to taxes and other one-time, unusual expenses. The profit and loss (P&L) statement is a financial statement that summarizes the revenues, costs, and expenses incurred during a specified period, usually a fiscal quarter or year.
How Does a Statement of Operations Work?
This analysis reveals, for example, what percentage of sales is thecost of goods sold and how that value has changed over time. Common size financial statements commonly include the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Essentially, the different measures of profitability in a multiple-step income statement are reported at four different levels in a business’ operations – gross, operating, pre-tax and after-tax.
It’s because the culmination of the report is a total net income or loss for the period. Accountants can arrive at this number after including additional non-operating activities such as financing and investing income or expense.