Selling stock results in cash income, which increases the company’s assets. This is the opposite of what happens when a business borrows money to meet expenses.
The total amount of cash distributed by cash dividends is charged against, and reduces, the retained earnings of the company, and thus decreases stockholders’ equity. Cash dividends in the United States are taxed at a lower rate than is ordinary income. Also known as return on net worth, a company’s return on equity (ROE) is a common metric used by investors to analyze profitability. Expressed as a percentage, ROE is calculated by dividing a company’s’ net income for the previous year by its shareholders’ equity.
Instead, the corporation likely used the cash to acquire additional assets in order to generate additional earnings for its stockholders. In some cases, the corporation will use the cash from the retained earnings to reduce its liabilities.
Interest payments to creditors are tax-deductible, but dividend payments to shareholders are not. Thus, a higher proportion of debt in the firm’s capital structure leads to higher ROE. Financial leverage benefits diminish as the risk of defaulting on interest payments increases. If the firm takes on too much debt, the cost of debt rises as creditors demand a higher risk premium, and ROE decreases. Increased debt will make a positive contribution to a firm’s ROE only if the matching return on assets (ROA) of that debt exceeds the interest rate on the debt.
The additional paid-in capital sub-account includes the value of the stock above its par value. If ABC’s stock has a par value of $1, then the common stock sub-account is increased by $50,000 while the remaining $700,000 is listed as additional paid-in capital.
Since stockholders’ equity is equal to assets minus liabilities, any reduction in stockholders’ equity must be mirrored by a reduction in total assets, and vice versa. The stockholder equity section of ABC’s balance sheet shows retained earnings of $4 million. When the cash dividend is declared, $1.5 million is deducted from the retained earnings section and added to the dividends payable sub-account of the liabilities section. The company’s stockholder equity is reduced by the dividend amount, and its total liability is increased temporarily because the dividend has not yet been paid.
Is a Common Stock Considered an Asset?
Borrowing creates a new liability and drives down stockholders’ equity. However, borrowing does not force the company to sell off ownership control, as selling stock does.
When a company talks about stockholders’ equity, it means the total amount of capital a company has received from investors in exchange for shares in the company. It represents all the assets in the company that investors own outright. Almost all profit-making companies have as their objective “to increase shareholder value,” which basically means the company is in business to increase the shareholders’ equity.
Stockholders Equity
As a result, it is difficult to identify exactly where the retained earnings are presently. Retained earnings are the portion of net income the company keeps instead of paying out to stockholders as dividends. For a firm that has been in business for a long time, retained earnings may be the largest entry on a statement of shareholders’ equity. The statement of shareholders’ equity states the retained earnings at the start of the year, net income, dividends paid and the amount of retained earnings at the end of the year. The common stock sub-account includes only the par, or face value, of the stock.
Stakeholders equity wrap up
This is a complicated exercise, however, since multiple transactions can decrease stockholders’ equity, including favorable transactions such as paying out stock dividends. When a company issues shares of common and preferred stock, the shareholder’s equity section of the balance sheet is increased by the issue price of the shares. The par value may be shown as a separate line item from additional paid-in capital on the shares, or the balance may be totaled on the same line. A company may raise stockholder’s equity by issuing shares of capital to pay off its debts and reduce interest costs. In some cases, a rise in stockholders’ equity indicates that a company has sold additional shares of stock.
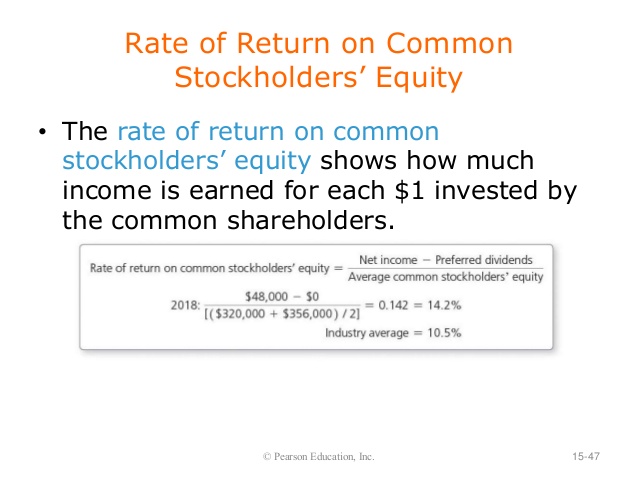
For example, if a company has net income of $1 million and total shareholders’ equity of $10 million, return on equity equals 0.1, or 10%. In most industries, a higher ROE makes the company more attractive for investors. Shareholders’ equity is the amount left over when you subtract a company’s liabilities from its assets. The Securities and Exchange Commission requires each publicly traded corporation to publish its statement of shareholders’ equity in its annual report. Stockholders’ equity depends on how a business values its assets in its financial statements.
Stockholders’ equity, also referred to as shareholders’ equity, is the remaining amount of assets available to shareholders after all liabilities have been paid. It is calculated either as a firm’s total assets less its total liabilities or alternatively as the sum of share capital and retained earnings less treasury shares. Stockholders’ equity might include common stock, paid-in capital, retained earnings and treasury stock.
- The statement of shareholders’ equity is part of a company’s balance sheet, which it issues to its shareholders on a quarterly or annual basis.
- The components of stockholders’ equity include the par value of outstanding shares, the amount of retained earnings, the value of any treasury stock and any additional paid-in capital.
When dividends are actually paid to shareholders, the $1.5 million is deducted from the dividends payable subsection to account for the reduction in the company’s liabilities. The cash sub-account of the assets section is also reduced by $1.5 million.
The components of stockholders’ equity include the par value of outstanding shares, the amount of retained earnings, the value of any treasury stock and any additional paid-in capital. The statement of shareholders’ equity is part of a company’s balance sheet, which it issues to its shareholders on a quarterly or annual basis.
Retained earnings refers to the money the company has made that it has not paid out as dividends. Rather, the company has elected to hold onto this money to finance its operations and repay debt. Retained earning, including net income for the current year, make up part of stockholders’ equity. Retained earnings reports the firm’s cumulative net income from inception to the most recent accounting period. If a corporation operates at a loss, stockholders’ equity decreases because the current year’s net income reduces retained earnings.
Companies may return a portion of stockholders’ equity back to stockholders when unable to adequately allocate equity capital in ways that produce desired profits. This reverse capital exchange between a company and its stockholders is known as share buybacks. Shares bought back by companies become treasury shares, and their dollar value is noted in the treasury stock contra account.
Treasury shares continue to count as issued shares, but they are not considered to be outstanding and are thus not included in dividends or the calculation of earnings per share (EPS). Treasury shares can always be reissued back to stockholders for purchase when companies need to raise more capital. If a company doesn’t wish to hang on to the shares for future financing, it can choose to retire the shares. The DuPont formula, also known as the strategic profit model, is a common way to decompose ROE into three important components. Essentially, ROE will equal the net profit margin multiplied by asset turnover multiplied by financial leverage.

Splitting return on equity into three parts makes it easier to understand changes in ROE over time. For example, if the net margin increases, every sale brings in more money, resulting in a higher overall ROE. Similarly, if the asset turnover increases, the firm generates more sales for every unit of assets owned, again resulting in a higher overall ROE. Finally, increasing financial leverage means that the firm uses more debt financing relative to equity financing.
The net effect of the stock dividend is simply an increase in the paid-in capital sub-account and a reduction of retained earnings. The stockholders’ equity can be calculated from the balance sheet by subtracting a company’s liabilities from its total assets. Although stock splits and stock dividends affect the way shares are allocated andthe company share price, stock dividends do not affect stockholder equity.
Stockholders’ equity – What is stockholders’ equity?
Companies fund their capital purchases with equity and borrowed capital. The equity capital/stockholders’ equity can also be viewed as a company’s net assets (total assets minus total liabilities). Investors contribute their share of (paid-in) capital as stockholders, which is the basic source of total stockholders’ equity. The amount of paid-in capital from an investor is a factor in determining his/her ownership percentage.
The amount transferred is equal to the number of shares distributed in the stock dividend multiplied by the price per share on the dividend date. This value per share of the dividend shares reduces the price of pre-dividend shares – shareholders end up with more shares of cheaper stock. When a company sells shares of stock, the sale price is often greater than the par value. The money paid by investors over and above the par value of the shares sold is listed on the statement of shareholders’ equity as additional paid-in capital. You will find additional paid-in capital entries corresponding to the entries for the par values of common stock, preferred stock and newly sold shares.
Just as selling stock raises the value of shareholders’ equity, it also creates new shareholders to share in that equity. Dividends may be paid in additional shares of stock rather than in cash. This is usually done via a special distribution in addition to the regular cash dividend.
When a dividend is declared, the total value is deducted from the company’s retained earnings and transferred to a temporary liability sub-account called dividends payable. This means the company owes its shareholders money but has not yet paid. When the dividend is eventually distributed, this liability is wiped clean and the company’s cash sub-account is reduced by the same amount. Regular dividends are made in cash and can be distributed quarterly, semi-annually or annually. If you own 1,000 shares and the total annual dividend is $1 per share, you will receive $1,000 in dividend income for the year.
Retained earnings are the earnings a business keeps to invest in itself instead of issuing cash dividends to stockholders; these also cause stockholders’ equity to rise. An increase in stockholders’ equity on the balance sheet along with a decrease in the dividend rate points to greater retained earnings. A company’s retained earnings include cash reserves and money spent to acquire new assets as well as money it uses to pay off debt, each of which directly increases stockholders’ equity. Stockholders’ equity includes retained earnings, paid-in capital,treasury stock, and other accumulative income.
What is Stockholders equity on balance sheet?
Stockholders’ equity is the total amount of capital given to a company by its shareholders in exchange for stock, plus any donated capital or retained earnings. In other words, stockholders’ equity is the total amount of assets that the investors will own once debts and liabilities are paid off.