The FASB’s Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 162 provides a detailed explanation of the hierarchy. Some of the basic accounting terms that you will learn include revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows. You will become familiar with accounting debits and credits as we show you how to record transactions.
accounting
In cash-basis accounting, cash earnings include checks, credit-card receipts, or any other form of revenue from customers. GAAP is a common set of accounting principles, standards, and procedures that public companies in the U.S. must follow when they compile their financial statements. International Accounting Standards are an older set of standards that were replaced by International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) in 2001.
Popular ‘Accounting & Auditing’ Terms
What account means?
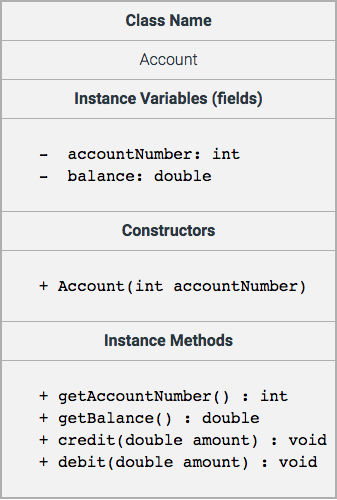
In accounting, an account is a record in the general ledger that is used to sort and store transactions. For example, companies will have a Cash account in which to record every transaction that increases or decreases the company’s cash.
This field is concerned with the aggregation of financial information into external reports. There are several career tracks involved in financial accounting. There is a specialty in external reporting, which usually involves a detailed knowledge of accounting standards. There is also the controller track, which requires a combined knowledge of financial and management accounting.
The annual report contains the independent auditor’s opinion as to the fairness of the financial statements, as well as information about the company’s activities, products, and plans. Typically, the best place to find these reports for a public company can be on their website under the Investor relations section. Financial statements used by external entities are prepared using generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP.
If a corporation’s stock is publicly traded, its financial statements must adhere to rules established by the U.S. The SEC requires that publicly traded companies in the U.S. regularly file GAAP-compliant financial statements in order to remain publicly listed on the stock exchanges. GAAP compliance is ensured through an appropriate auditor’s opinion, resulting from an external audit by a certified public accounting (CPA) firm. GAAP may be contrasted with pro forma accounting, which is a non-GAAP financial reporting method. Internationally, the equivalent to GAAP in the United States is referred to as international financial reporting standards (IFRS).
Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) refer to a common set of accounting principles, standards, and procedures issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB). Public companies in the United States must follow GAAP when their accountants compile their financial statements.
n an itemized statement of money owed for goods or services
- There is a specialty in external reporting, which usually involves a detailed knowledge of accounting standards.
- This field is concerned with the aggregation of financial information into external reports.
- There are several career tracks involved in financial accounting.
GAAP is a combination of authoritative standards (set by policy boards) and the commonly accepted ways of recording and reporting accounting information. GAAP aims to improve the clarity, consistency, and comparability of the communication of financial information.
You will also see why two basic accounting principles, the revenue recognition principle and the matching principle, assure that a company’s income statement reports a company’s profitability. IFRS is a set of international accounting standards, which state how particular types of transactions and other events should be reported in financial statements. Generally accepted accounting principles refer to a common set of accepted accounting principles, standards, and procedures that companies and their accountants must follow when they compile their financial statements.
Their role is to define how your company’s money is spent or received. Each category can be further broken down into several categories.
IFRS is followed in over 120 countries, including those in the European Union (EU). There are five main types of accounts in accounting, namely assets, liabilities, equity, revenue and expenses.
If he uses the cash-basis accounting method, because no cash changes hands, the carpenter doesn’t have to report any revenues from this transaction in 2004. But say he lays out the cash for his expenses in 2004. In this case, his bottom line is $1,200 less with no revenue to offset it, and his net profit (the amount of money the company earned, minus its expenses) for the business in 2004 is lower. This scenario may not necessarily be a bad thing if he’s trying to reduce his tax hit for 2004. For example, if a painter completed a project on December 30, 2003, but doesn’t get paid for it until the owner inspects it on January 10, 2004, the painter reports those cash earnings on her 2004 tax report.
Primary Meanings of account
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are a set of international accounting standards, which state how particular types of transactions and other events should be reported in financial statements. IFRS are issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), and they specify exactly how accountants must maintain and report their accounts. The standards that govern financial reporting and accounting vary from country to country.
In the United States, financial reporting practices are set forth by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and organized within the framework of the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). General-purpose financial statements provide much of the information needed by external users of financial accounting. These financial statements are formal reports providing information on a company’s financial position, cash inflows and outflows, and the results of operations. Many companies publish these statements in annual reports, also known as a 10-K or a 10-Q (quarterly report).
n a statement that makes something comprehensible by describing the relevant structure or operation or circumstances etc.
We will discuss the language of GAAP further in later sections. The Statement of Financial Accounting Concepts is issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and covers financial reporting concepts. GAAP is a common set of accepted accounting principles, standards, and procedures that companies and their accountants must follow when they compile their financial statements. The international alternative to GAAP is the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), set by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). Accountants are directed to first consult sources at the top of the hierarchy and then proceed to lower levels only if there is no relevant pronouncement at a higher level.
Statements of Financial Accounting Standards were published by the Financial Accounting Standards Board to provide guidance on specific accounting topics. “Acceptance From Foreign Private Issuers of Financial Statements Prepared in Accordance With International Financial Reporting Standards Without Reconciliation to U.S. GAAP,” Page 7. “Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 162.” Accessed Oct. 3, 2019. There is plenty of room within GAAP for unscrupulous accountants to distort figures. So, even when a company uses GAAP, you still need to scrutinize its financial statements.